Good Evening,
As we move through the ever-changing landscape that is the Chinese energy policy, its not often you stumble upon a development that is under the radar, interesting, productive and universally positive.
China’s growing use of gas in its economy is exactly that. Given all the noise around wind, solar and nuclear, teh fact that China is also being very aggressive with gas often goes underreported. Also the die hards forget that it was the shift to natty that made the US’s carbon usage peak and decline since the late 90s - China is following in those very footsteps (at the very least it embarked on the path).
Similarly it’s interesting because one has to balance out a lot of moving parts - domestic policy, industrial usage, LNG and its volumes to get the full picture. But it’s well worth doing as figuring this market development out really does open the door to exciting new growth areas for companies we don’t associate with them.
But before we dive in, some admin. This is the second week of our Energy focus here, and we’re starting with PetroChina and the gas market. Refiners are next later this week. We are also working on a bonus write up on a company we like a lot, and would like others to at least be more aware of it, this is likely coming next Sunday (the 14th of January).
As mentioned in the opening piece, majority of the Energy content is paywalled, as this is my specialist subject after all. This is a bit of an exception, as the paywall starts about half way through the piece. The Gas market writeup is free, the PetroChina focus is for premium subscribers. We believe this strikes the right balance between providing reliable information and ideas to those who value it the most, while also contributing to the better understanding of Chinese policies in the space to the broader public.
As ever if you want to hop over the paywall, by all means feel free to do thusly. The stronger the economic signal, the more committed to this project we can be over the longer term.
A quick reminder that there are only 2 days left to take advantage of the Winter Festive Season Promotional Extravaganza. Subscription discounts apply all the way through the 7th of January (Eastern Orthodox Christmas) and thats is.
The only other reminder is to be on the lookout for the new episode of the Pandacast, should be available on Monday for your listening pleasure.
**Important Reminder: Nothing in this Substack is Investment Advice. This information is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or other advice. Any examples used are for illustrative purposes only and do not reflect actual recommendations. Please consult a licensed financial advisor or conduct your own research before making any investment decisions. The authors, publishers, and affiliates of this content do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or suitability of the information and are not responsible for any losses, damages, or actions taken based on this information. Past performance is not indicative of future results.**
Back to the regularly scheduled programing.
China Natural Gas Market
China's natural gas market is undergoing a significant structural transformation, driven by policy support, infrastructure development, and evolving market mechanisms. We look in to what those are and try and make sense of it.
Market Structure and Supply Dynamics
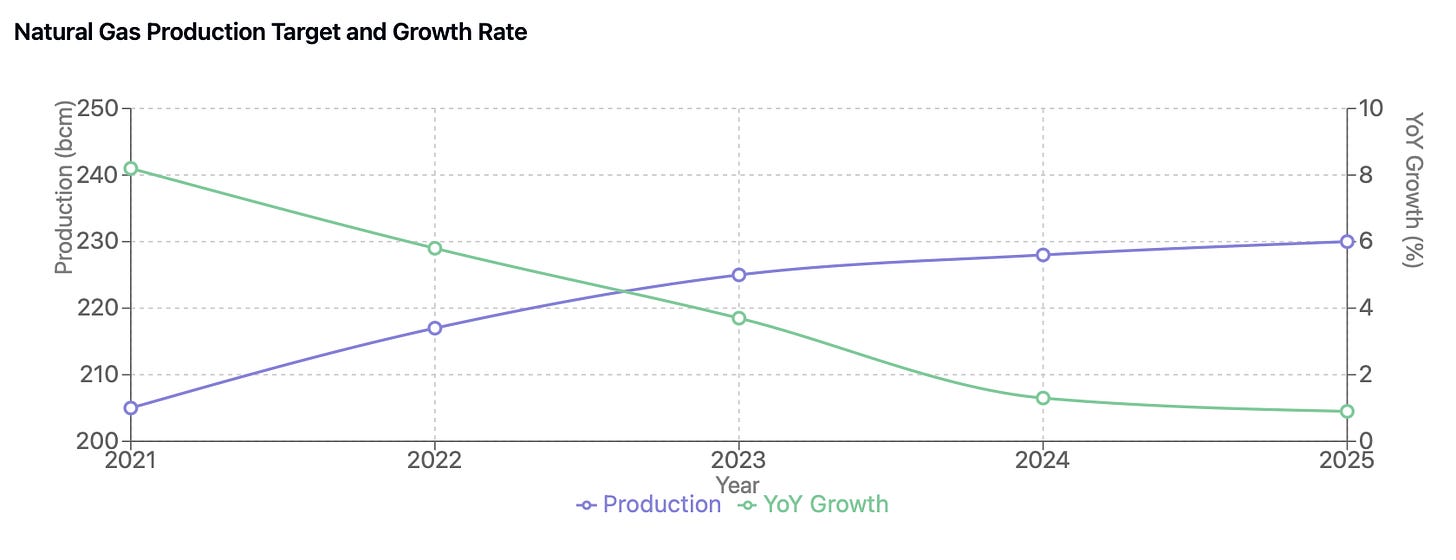
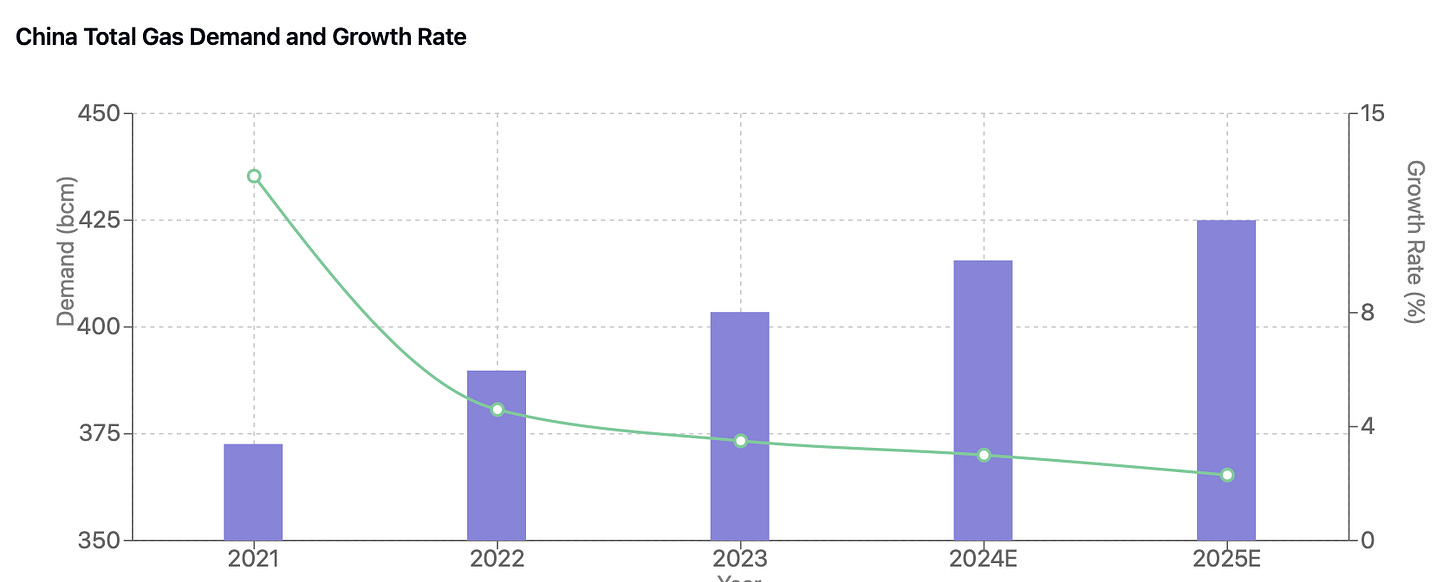
The Chinese natural gas market continues to demonstrate robust growth momentum, underpinned by strategic national initiatives and infrastructure development. Production targets set under the 14th Five-Year Plan aim to exceed 230 billion cubic meters by 2025, forming a crucial component of China's broader energy security strategy. This production goal aligns with the national objective to boost domestic energy production capacity beyond 4.6 billion tons of standard coal equivalent.
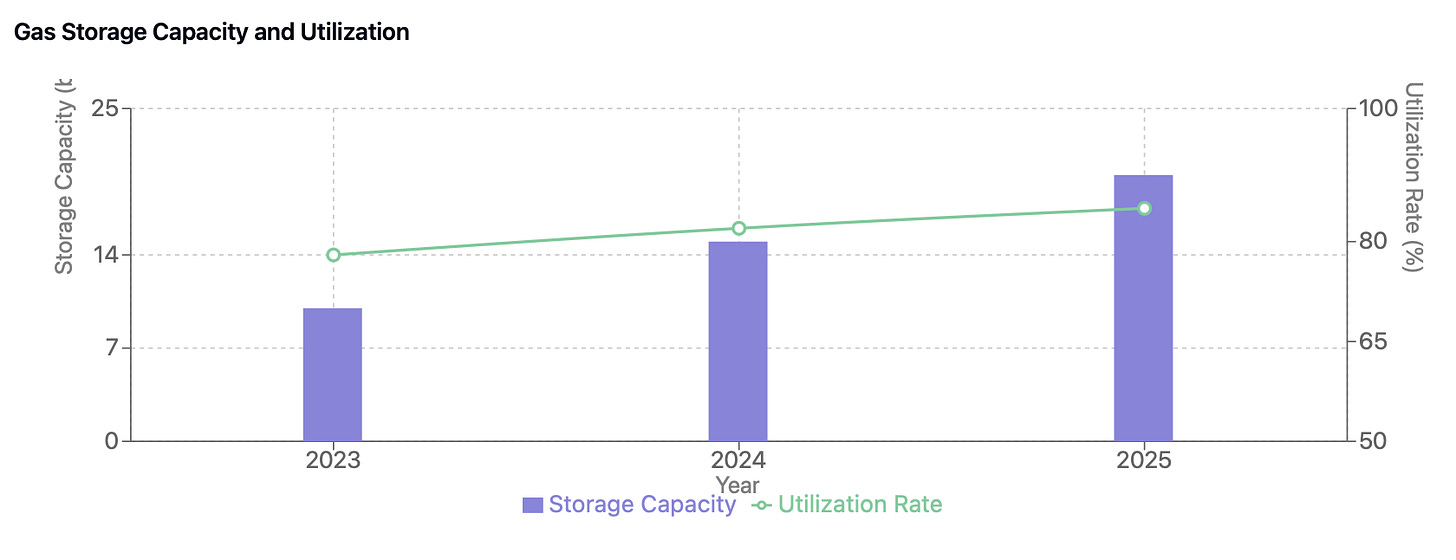
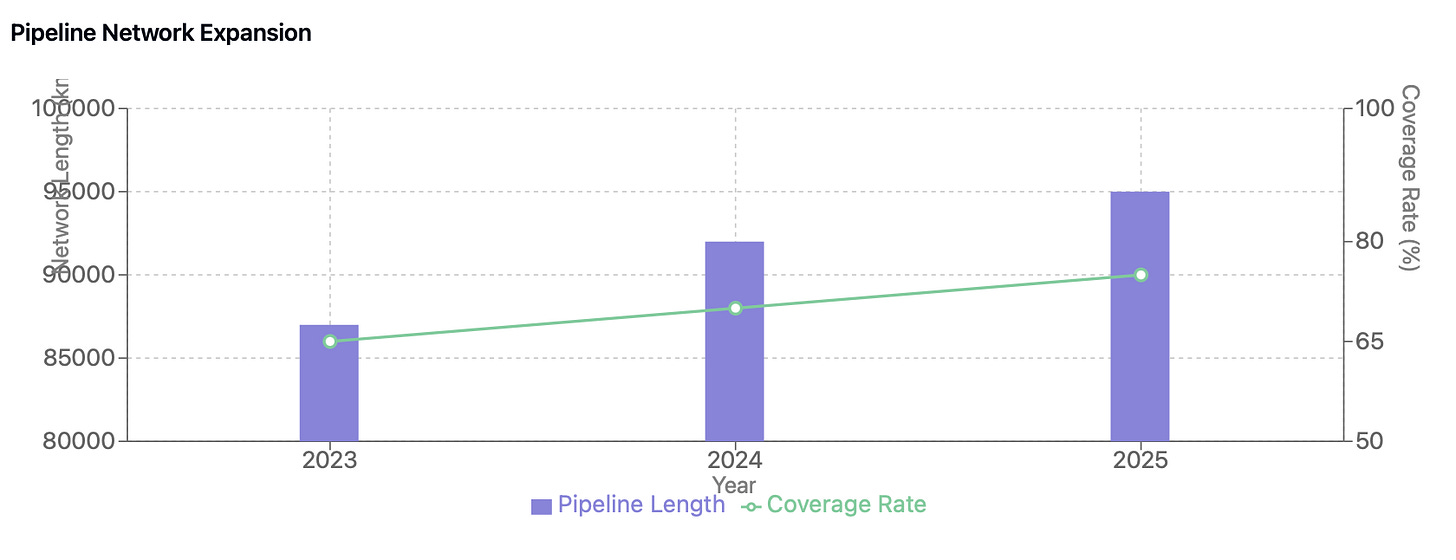
Infrastructure development stands as a key enabler of market growth. China's natural gas infrastructure is undergoing significant expansion, underpinned by ambitious national development targets. Storage capacity is set to more than double, reaching over 20 billion cubic meters by 2025, with six major storage centers comprising 50 facilities under development nationwide. The pipeline network, dominated by PetroChina with approximately 87,000 kilometers of pipelines, forms the backbone of national gas distribution. This network is being strategically expanded, particularly in coastal economic zones and urban areas, improving both coverage and supply reliability.
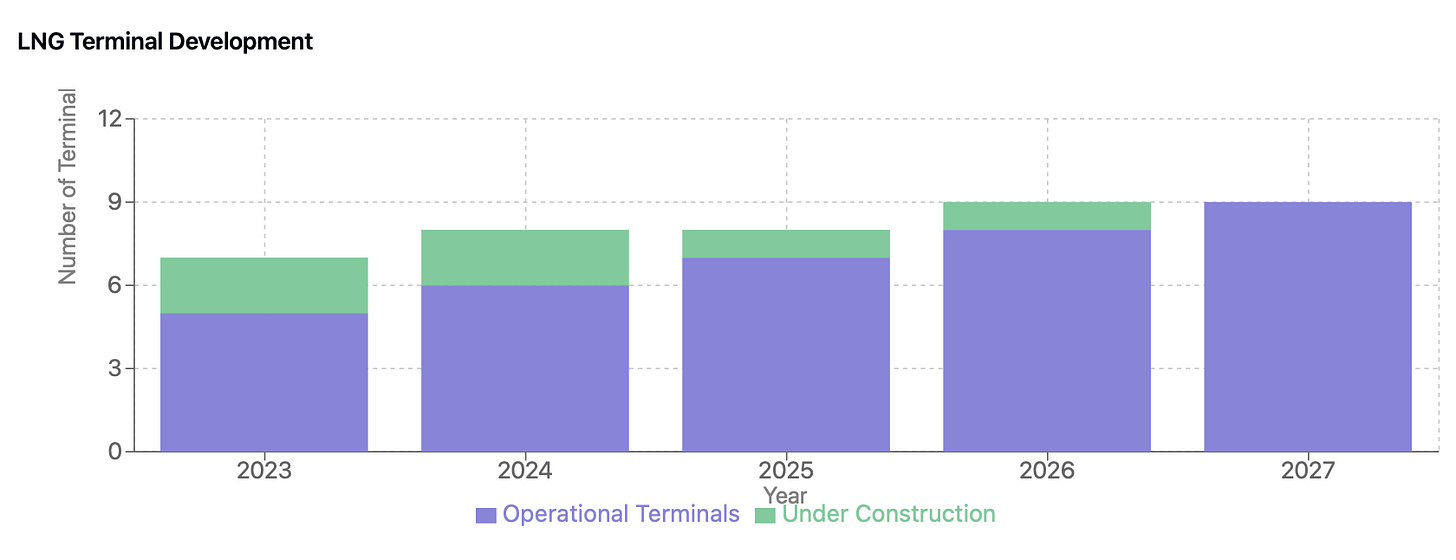
The infrastructure build-out includes significant LNG terminal developments, with utilization rates projected to rise from 78% in 2023 to exceed 85% by 2025. A notable addition is the new Fujian terminal, scheduled for operation by mid-2027. Current infrastructure efficiency metrics show steady improvement, with storage facility utilization rates increasing and pipeline network coverage expanding to support growing urban and industrial demand. This comprehensive infrastructure expansion is critical for managing seasonal demand fluctuations and supporting the broader transition toward cleaner energy sources.
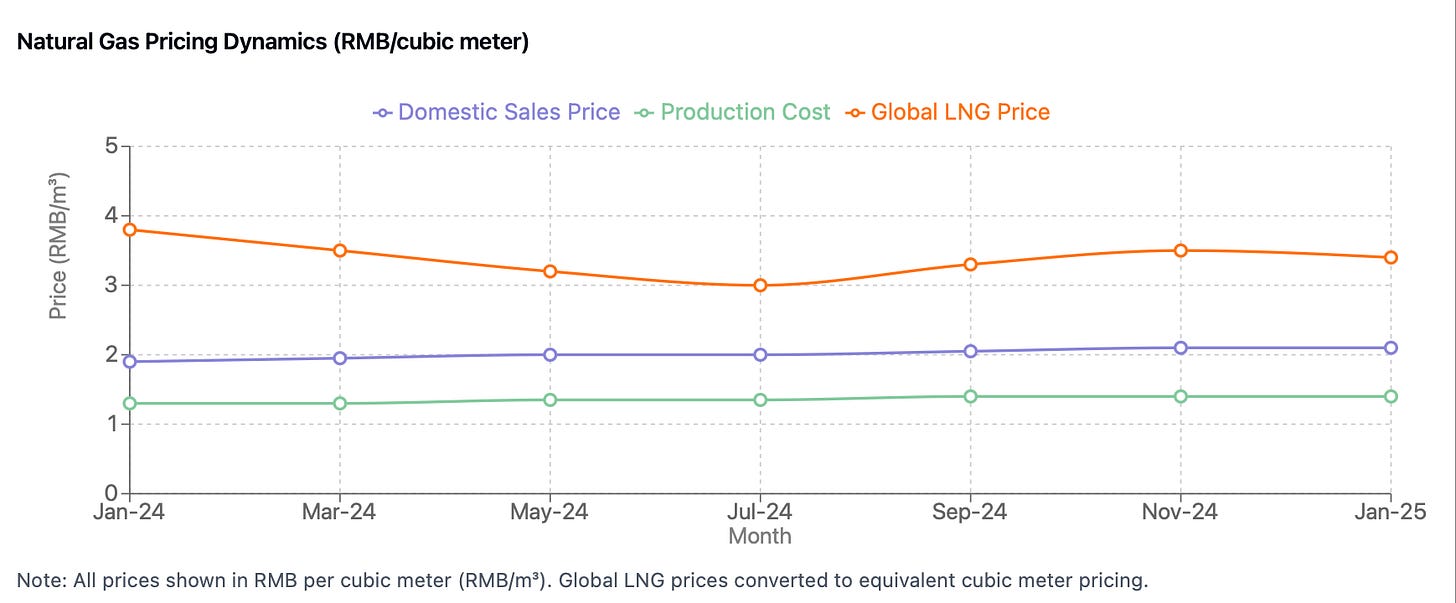
Production economics have shown marked improvement, with domestic gas production costs maintaining competitiveness at RMB 1.25-1.50 per cubic meter, significantly below import costs of RMB 2.50-3.00 per cubic meter. This cost advantage provides domestic producers with substantial operational flexibility and margin protection.
Demand Analysis and Market Segmentation
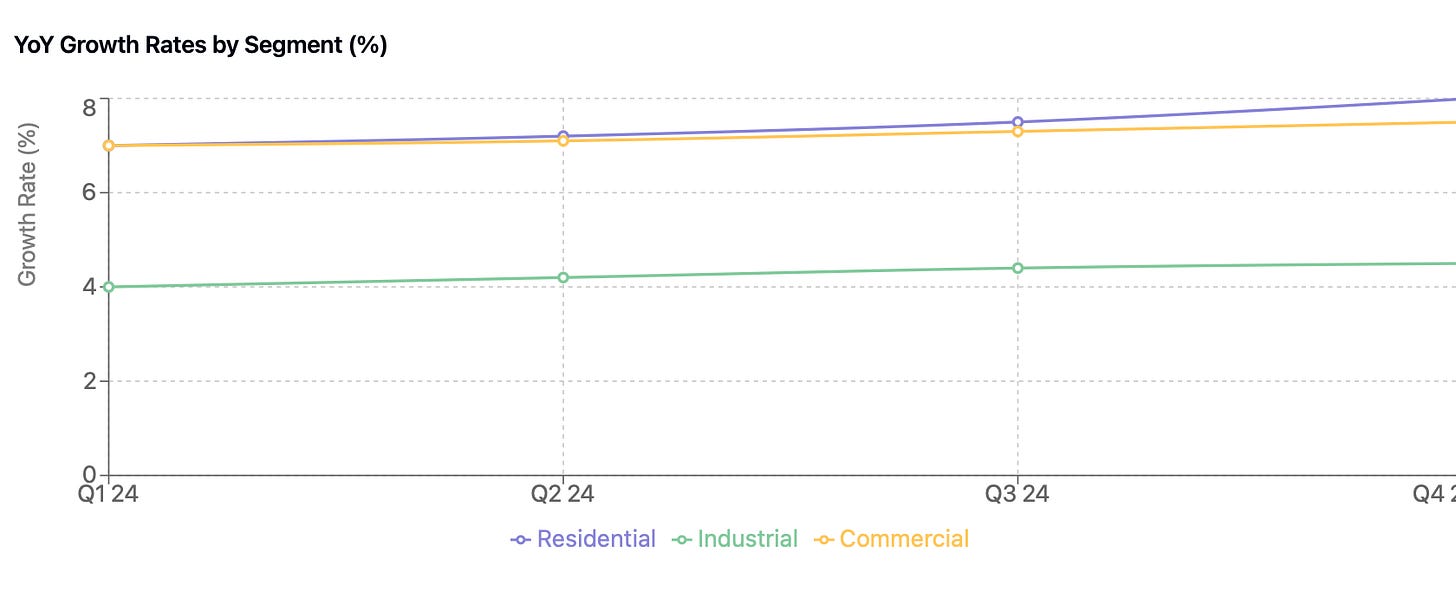
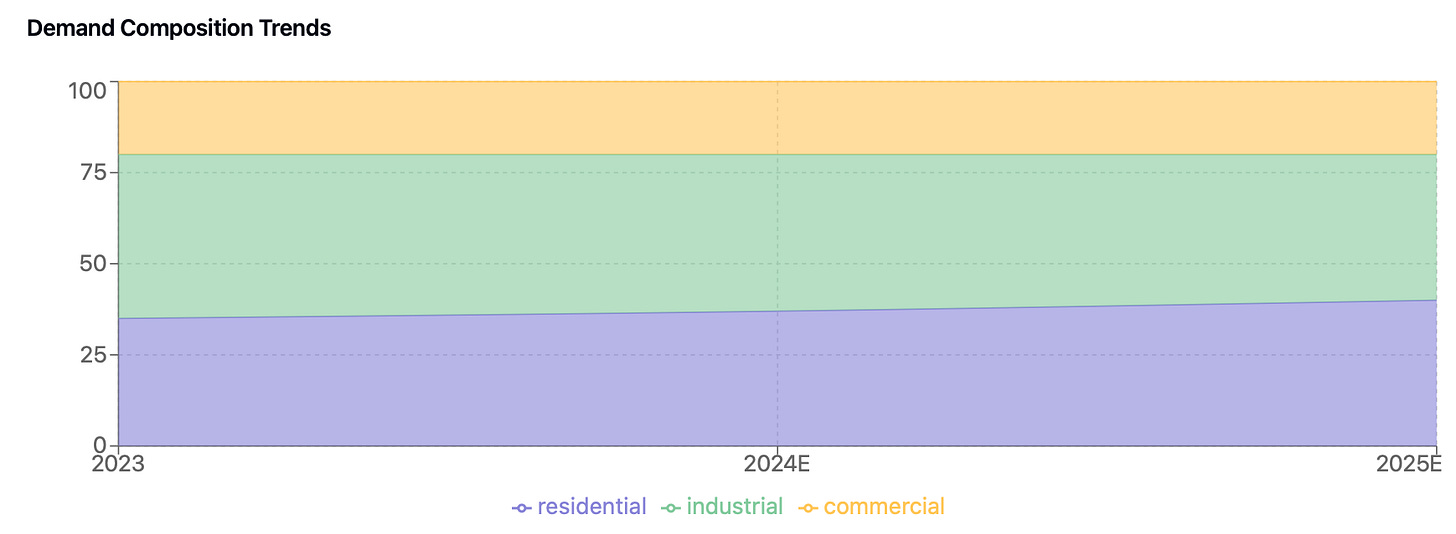
Demand patterns reveal distinct sectoral characteristics and growth trajectories. The residential sector has maintained steady momentum, recording 7% year-over-year growth in the first nine months of 2024. Urban gas connections continue to expand, supported by favorable policy frameworks and the ongoing implementation of price pass-through mechanisms targeted for completion by 2025.
Industrial consumption presents a more nuanced picture, with 4% year-over-year growth in 9M24. Sector-specific variations are notable, with petrochemicals and glass manufacturing showing particular strength, while property-related industries continue to face headwinds. Integrated energy projects have emerged as a significant growth driver, with major players like ENN targeting over 20% growth in IE volumes for FY25, particularly focusing on commercial users with decarbonization requirements.
The commercial sector has demonstrated robust growth of 7% year-over-year in 9M24, with particular strength in export-driven coastal regions. This growth benefits from expanding urban gas infrastructure and broader economic recovery in key regions.
Competitive Landscape and Market Leadership
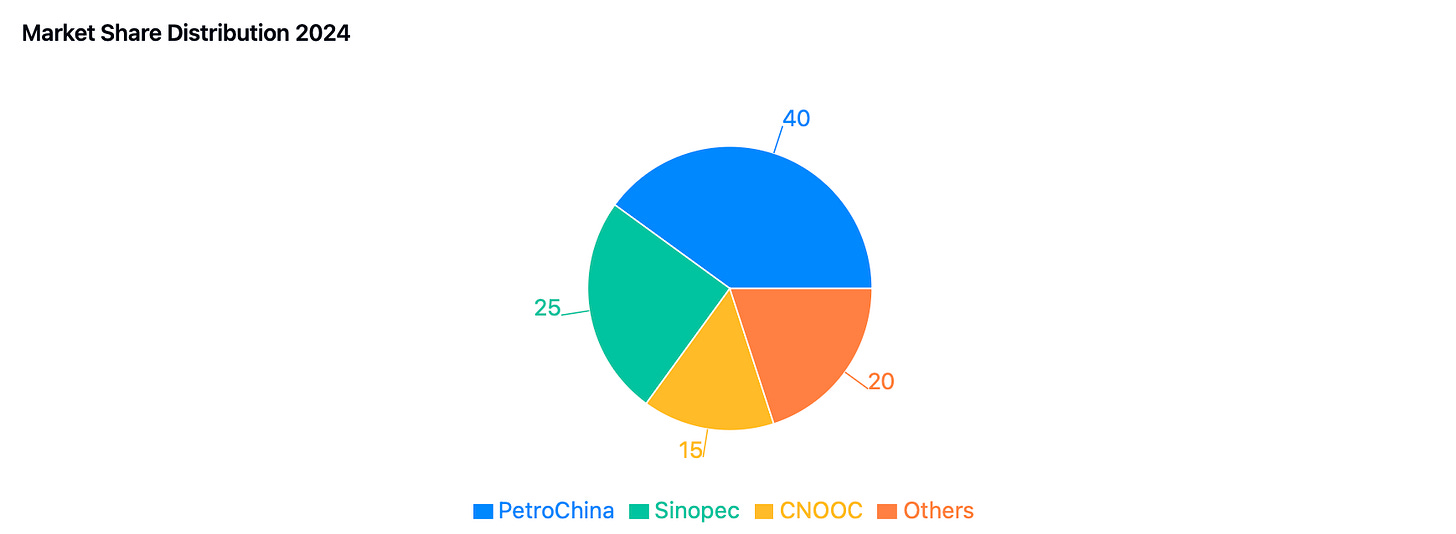
Market leadership remains concentrated among several key players, with PetroChina maintaining dominant market share exceeding 40%. The company's strategic focus on natural gas is evidenced by projections for gas to contribute approximately 40% of E&P EBIT by 2025, supported by ambitious infrastructure expansion plans including doubling storage capacity to over 20 billion cubic meters by 2025.
ENN Energy has demonstrated strong operational execution, reporting 5% retail gas volume growth in the first ten months of 2024, with acceleration to over 6% in October. The company maintains positive full-year guidance exceeding 5% year-over-year growth, while targeting stable dollar margins around RMB 0.54 per cubic meter.
CR Gas similarly exhibits healthy growth metrics, with retail volume increasing approximately 5% in 9M24 and full-year guidance of 6-8% year-over-year growth. The company's dollar margin target of RMB 0.53-0.54 per cubic meter aligns with broader market trends.
Regulatory Environment and Policy Framework
China’s natural gas pricing mechanisms have been evolving toward greater market orientation, driven by government-led reforms. A key element of this transition is the gradual liberalization of pricing, where city-gate prices are now linked to a basket of alternative fuels such as crude oil and LPG. This aligns domestic prices with global market trends. Additionally, industrial and commercial users enjoy greater flexibility, with suppliers able to negotiate prices based on supply-demand dynamics, enhancing responsiveness and competition in the sector.
The pricing structure operates under a dual-tiered system. Residential tariffs remain regulated to ensure affordability, particularly in urban centers and regions with high heating demand during winter. In contrast, industrial and commercial prices are largely market-driven, with liberalization enabling suppliers and users to set rates directly through contracts tailored to volume and seasonal demand.
Seasonal adjustments play a significant role in maintaining stability during peak demand periods, such as winter. Suppliers are incentivized to build inventories and deploy stored gas at capped prices, ensuring uninterrupted supply and preventing market disruptions. Meanwhile, the full residential price pass-through mechanism, set for full implementation by 2025, will enable suppliers to adjust tariffs directly in line with procurement costs. This reform reduces reliance on subsidies and enhances the financial sustainability of gas utilities.
Lastly, regional variations in pricing persist due to differences in transportation costs, pipeline access, and levels of urban infrastructure development. This disparity underscores the importance of robust infrastructure networks to minimize inefficiencies and achieve greater pricing uniformity across the country. Collectively, these mechanisms reflect a dynamic and adaptive approach to pricing, supporting the growth and sustainability of China’s natural gas sector.
The usage prioritization framework, introduced by the National Energy Administration (NEA) in June 2024, established a hierarchical system for natural gas allocation. This framework prioritizes household consumption to ensure availability and affordability for residential users. It also supports industrial and essential services such as hospitals, schools, and key industries, while imposing restrictions on non-essential usage, including gas-based methanol and petrochemical manufacturing. These measures promote more efficient allocation of natural gas resources.
In December 2024, methane emission controls were tightened to align with China’s commitments under the Global Methane Pledge. The regulations mandate the capture of methane for mines with concentrations exceeding 8%, with compliance deadlines set for April 2025 for new mines and April 2027 for existing operations. These rules are expected to significantly reduce methane emissions, which are a potent greenhouse gas.
Additionally, carbon reduction initiatives target a 1% reduction in emissions from key industries compared to 2023 levels and a 2.5% improvement in energy efficiency per unit of GDP in 2024. These initiatives incentivize efficient gas use across sectors and reflect China’s broader push for decarbonization and energy sustainability. Together, these regulatory enhancements underline the government’s commitment to creating a cleaner, more efficient energy system while supporting the growth of the natural gas sector.
Market Outlook and Strategic Implications
Near-term catalysts include the completion of residential price pass-through implementation, storage capacity expansion, and procurement optimization benefits. Longer-term growth drivers remain robust, encompassing continued urban infrastructure expansion, industrial decarbonization initiatives, and technological advancement.
The market demonstrates strong structural growth characteristics, supported by policy alignment, infrastructure development, and evolving market mechanisms. For sophisticated investors, the sector offers exposure to China's energy transition while maintaining attractive financial metrics and clear catalysts for value realization.
China's natural gas market continues to evolve toward greater sophistication, characterized by improving pricing mechanisms, expanding infrastructure, and clearer regulatory frameworks. The sector's strategic importance in China's energy transition, combined with attractive financial metrics and clear growth drivers, presents compelling opportunities for strategic investment consideration.
We will now discuss our preferred way of playing the theme: PetroChina. For all the non-premium subscribers, do upgrade if you are interested.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Panda Perspectives to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.