Merry Christmas! Happy Holidays! The Christmas spirit as well and truly set in, even though there are a few working days still left to go. Great time to release a 2025 preview for your perusal.
A few words on the structure: The 2025 Outlook will come out in 3 parts. This is Part One, a generally available preview of policy and economic numbers in China. I tried to make it as accessible and fun to read as I could. The second part of this will be to do with the stock market, and predictions thereof. Part Three is a broader Asia outlook, less granular but much broader. Most of those pieces will be for subscribers only. I would like to thus take the opportunity to invite people to take the plunge!
If you’re short on time, feel free to skip to the very end for a concise Panda Perspective summarizing the key points. That said, I’ve done my best to make the full article engaging, so I hope you’ll give it a read!
Technical note: I’m migrating to (or attempting a migration to) using python for charting, and it’s a bit of a learning curve, so apologies for formatting on some of them, realised that they get cropped weirdly a little late.
Now, without any further delays, let’s dive into the story of China in 2025:
China’s 2025 economic outlook feels like a high-stakes tightrope act, balancing cautious pragmatism with ambitious policy leaps. Growth forecasts waltz between 4.0% and 5.0%, with most pundits landing gracefully at 4.5%—a testament to careful planning rather than the adrenaline-fueled feats of yesteryear.
The year’s growth trajectory mimics a phoenix’s arc—dipping before soaring—buoyed by policy seeds sown at December’s Central Economic Work Conference. The second half of 2025 is poised to shine brighter, reaping the rewards of fiscal and monetary moves choreographed with precision.
In a twist worthy of a blockbuster, China is breaking tradition, expanding its fiscal deficit to 4% of GDP, and rolling out a jaw-dropping RMB 10 trillion in government bonds. Perhaps stealing the show is the long-overdue focus on stimulating consumption, finally taking center stage in the economic script.
Looking ahead to 2026, growth is expected to ease gently to 4.2% as structural transitions, global uncertainties, and property sector adjustments settle into the mix. It’s less of a heart-pounding sprint and more of a thoughtful marathon—where quality and sustainability take the podium, leaving quantity to cheer from the sidelines.
Current State of Consumption: A Tale of Caution and Promise
In the grand theater of China's economy, retail sales have been playing a rather cautious tune in 2024, waltzing along at a modest 3% yearly pace. This reserved performance tells a story of consumers still tip-toeing through economic uncertainties, like careful dancers testing an unfamiliar floor. The property market's extended hibernation has cast a long shadow over consumer confidence, while households have been squirreling away savings like prudent forest creatures preparing for winter.
Yet amidst this cautious choreography, some bright spots have emerged. The final act of 2024 saw a flourish of activity in premium purchases - from sleek home appliances to gleaming electric vehicles - suggesting that Chinese consumers haven't lost their appetite for quality, merely their immediate willingness to feast.
The household spending narrative reads like a tale of two cities. On one side, we find the weight of declining property values pressing on perceived wealth like a heavy winter coat, while on the other, income growth remains as frozen as a December morning for many lower-income groups. The savings rate hovers stubbornly around 35% - a testament to the Chinese consumer's legendary patience and prudence in uncertain times.
Meanwhile, government support plays a supporting role rather than taking center stage. While public spending on social welfare - the trinity of healthcare, pensions, and housing subsidies - has grown by a respectable 7% year-over-year, it's more of a gentle breeze than the gale force needed to fully unfurl the sails of consumer spending.
This complex tapestry of consumer behavior suggests an economy in transition, where caution and potential exist in equal measure, waiting for the right moment to find their balance.
Policy Proposals Impacting Consumption
Direct Consumer Support:
Subsidies for Durable Goods:
Expansion of trade-in subsidies for appliances and automobiles.
Inclusion of mobile devices in subsidy programs .
Real Estate-Linked Policies:
Reduced down-payment requirements for first-time homebuyers.
Housing subsidies targeted at low-income families to unlock demand .
Social Safety Nets:
Enhanced healthcare coverage and pension increases to reduce precautionary savings.
Fertility and childcare subsidies aimed at supporting family-related expenses and encouraging broader spending .
Promoting Novel Consumer Services:
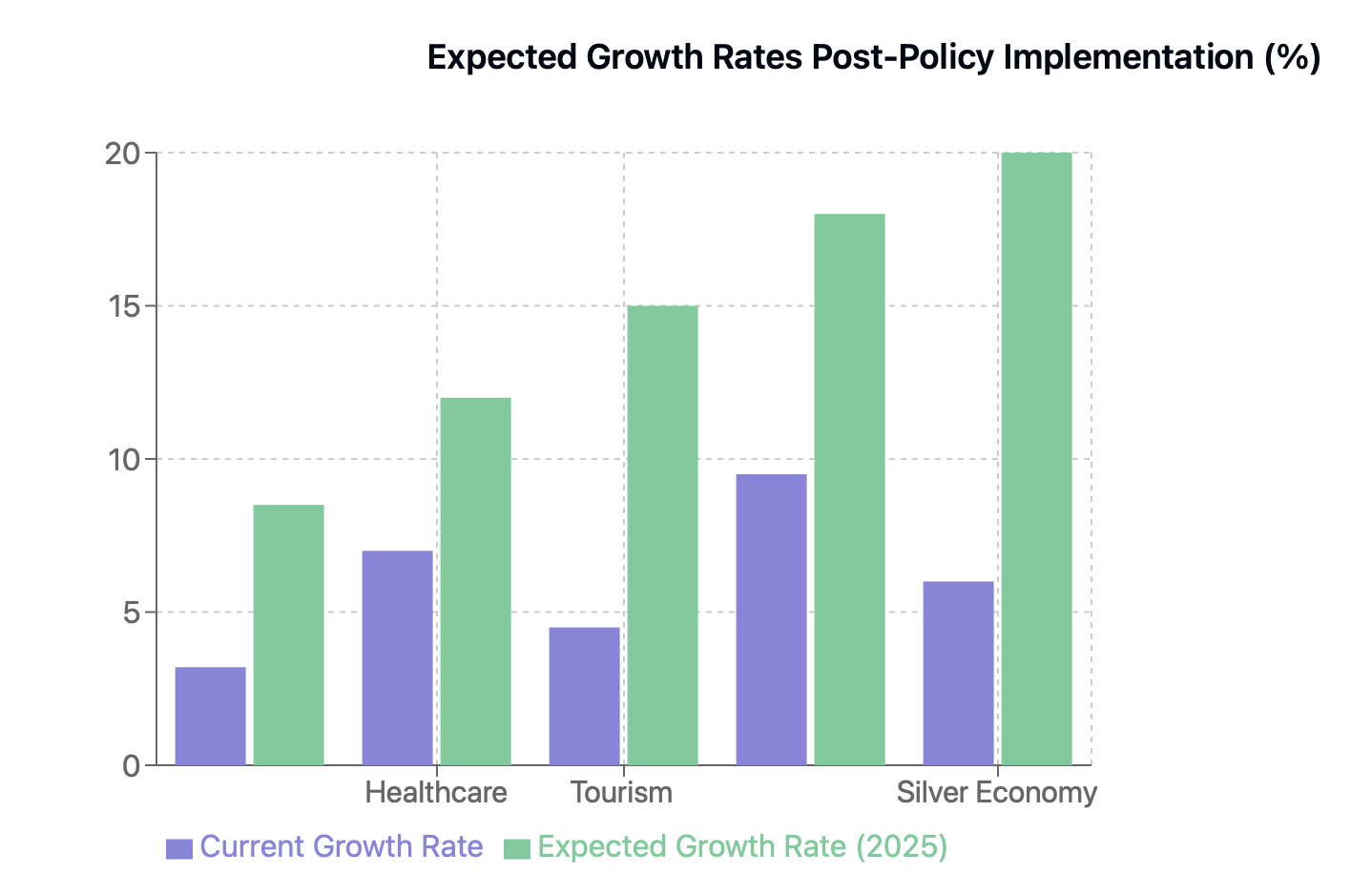
Development of the “Silver Economy” (services targeting seniors) and “Snow Economy” (winter tourism), leveraging underexplored areas to drive spending.
Government incentives to encourage spending in tourism, culture, and digital services .
Tax Incentives and Transfers:
Personal income tax reforms to increase disposable income, particularly for middle-income households.
Targeted transfers to rural and lower-income families to address consumption inequality .
Public Spending:
Increased government consumption in education, healthcare, and public services to stimulate demand indirectly .
Predictions for 2025 Consumption: A Tale of Cautious Optimism
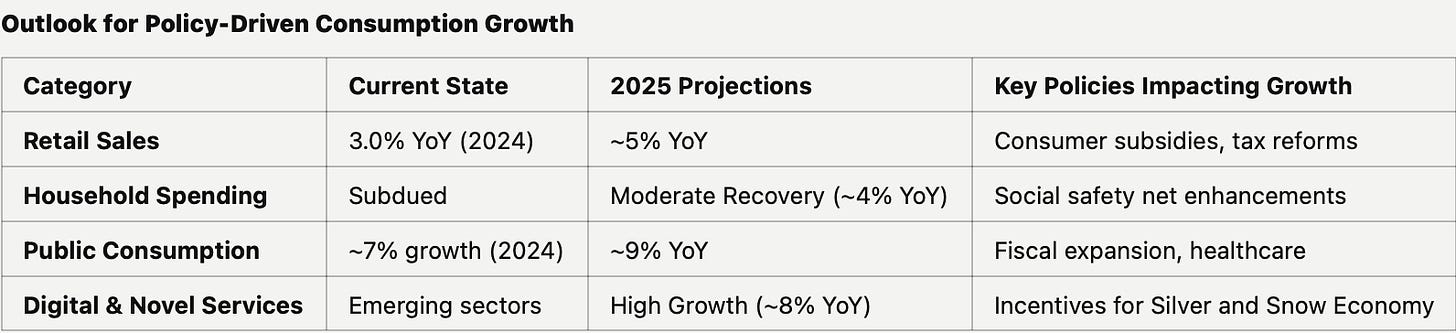
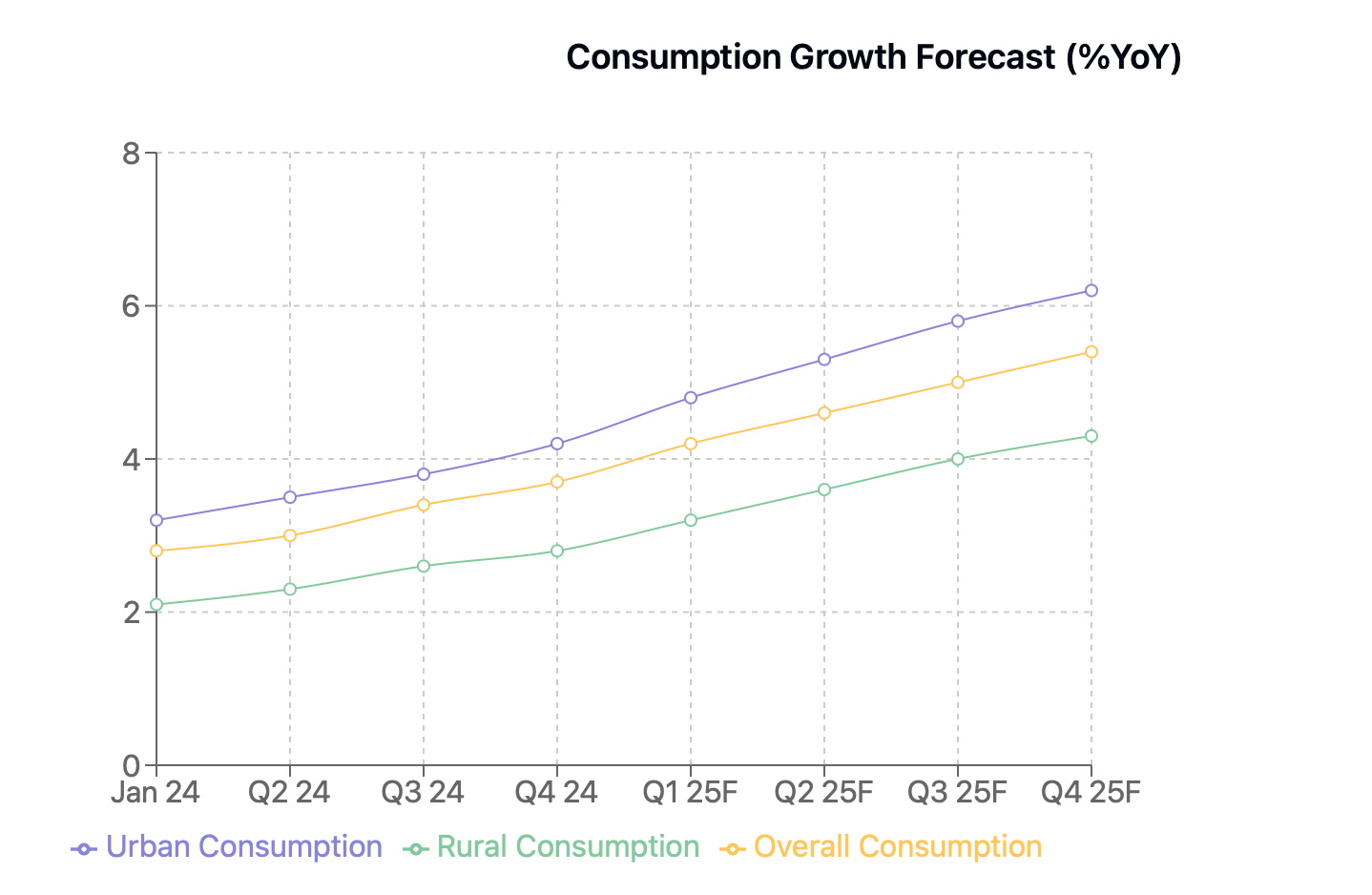
Like a spring thaw after a long winter, China's consumption landscape in 2025 promises a gradual but meaningful awakening. Retail sales are expected to blossom to around 5% year-over-year growth, painting a more vibrant picture than 2024's muted performance. Urban areas, nourished by targeted subsidies and renewed confidence, will likely lead this renaissance, while rural spending finds its footing on the fertile ground of agricultural support.
Household spending appears poised for a moderate renaissance, like a carefully choreographed dance between rising incomes and gradually declining savings rates. The spotlight shines particularly bright on discretionary spending - imagine electronics stores humming with activity and entertainment venues finding their rhythm once again.
Government consumption steps onto the stage with considerable gravitas, expected to contribute a substantial 1.5 percentage points to GDP growth. This performance features an ensemble cast of increased public service spending and fiscal transfers, creating a steady backbeat for broader economic growth.
In terms of sectoral impact, we're watching a quartet of stars emerge: consumer durables striking bold notes, tourism embarking on ambitious journeys, healthcare services providing steady harmony, and digital platforms orchestrating new consumption symphonies.
Yet, like any compelling narrative, challenges provide dramatic tension. Income inequality between rural and urban areas looms like a shadow in the wings, threatening to mute the performance's reach. Meanwhile, the property market's continued pas de deux with uncertainty may keep upper-middle-class wallets in their pockets longer than hoped.
The story of 2025's consumption thus reads like a carefully balanced novel - one where hope and caution trade chapters, and success depends on how well policymakers can edit the narrative as it unfolds.
Current State of Fixed Asset Investment (FAI)
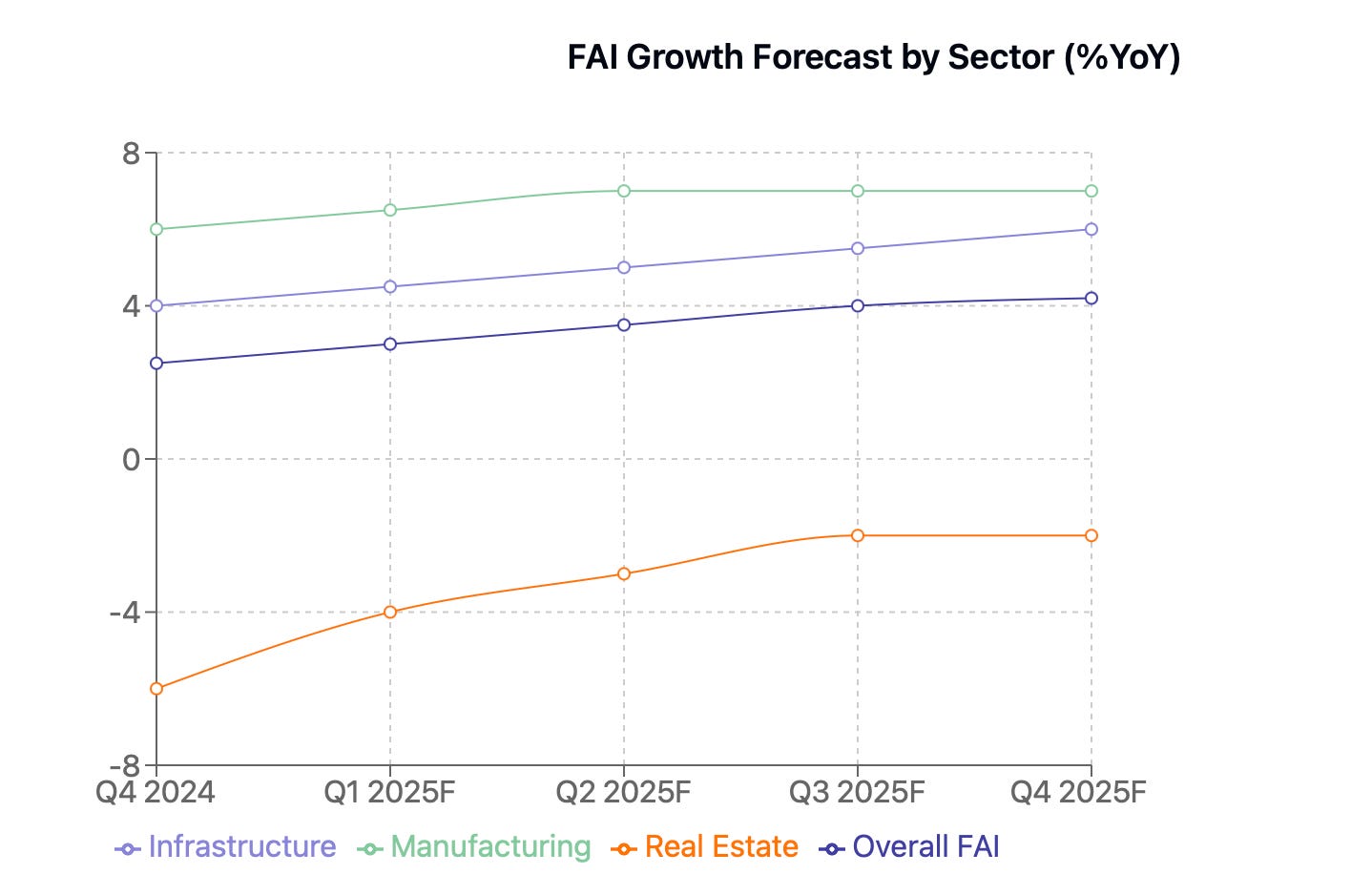
China's fixed asset investment landscape for 2025 presents an intricate blueprint of transformation and renewal. After 2024's modest performance waltz of 2.5% growth, the stage is set for a more dynamic performance, with overall FAI expected to pirouette to 4.2% growth in 2025.
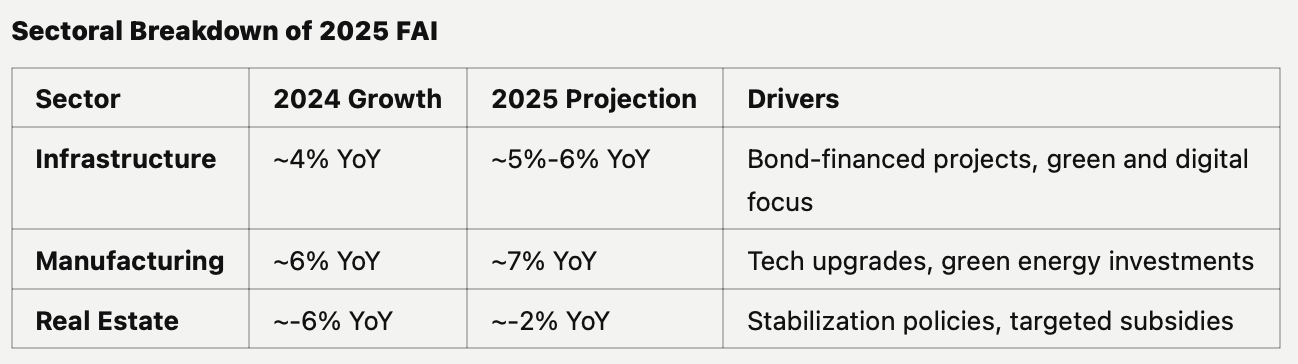
Infrastructure investment emerges as the prima ballerina, gracefully leaping to 5-6% growth. This performance features a fascinating pas de deux between traditional infrastructure, commanding 60% of the spotlight, and its emerging partner - green and digital infrastructure - which elegantly claims 40% of the stage, up from its supporting role of 25% in 2024.
Manufacturing investment choreographs an ambitious performance, targeting 7% growth with the precision of a technical virtuoso. This movement features a fascinating trio: high-tech manufacturing leading with 50% of the composition, green manufacturing harmonizing at 30%, and traditional manufacturing providing the foundational bass notes at 20%.
The real estate sector, though still performing in a minor key with a projected -2% growth, shows signs of finding its rhythm again, a marked improvement from 2024's more somber -6% performance. This gradual modulation suggests a carefully orchestrated transition rather than a sudden key change.
Behind these headline numbers, a fascinating subplot unfolds in the details. Picture 3,000 kilometers of new high-speed rail tracks weaving through the landscape like silver ribbons, while 50+ new metro lines bring urban ballets to Tier 2 and 3 cities. Meanwhile, in the digital realm, 3.5 million 5G base stations stand ready to conduct the symphony of tomorrow's connectivity, while 2.5 million EV charging stations prepare to power the green vehicle revolution.
Yet, like any complex performance, challenges provide dramatic tension. Local government debt plays the role of stern critic, while private sector confidence waits in the wings for its cue to return. The story's success will ultimately depend on how well policymakers can conduct this elaborate economic orchestra through its 2025 season.
Key Metrics:
Transport:
Planned high-speed rail extensions: 3,000 km of new track.
Urban metro projects: 50+ new lines in Tier 2/3 cities, focusing on connectivity.
Water Conservancy:
Flood control projects: Covering 30 million hectares.
Irrigation upgrades: Estimated increase in agricultural efficiency by 15%-20%.
Digital Infrastructure:
5G base stations: Expected to reach 3.5 million nationwide.
EV charging stations: 2.5 million units to support the green vehicle transition.
Policy Integration:
Green Goals: Aligned with China’s carbon neutrality by 2060, focusing on sustainable urbanization and transport decarbonization.
15th Five-Year Plan (FYP): Sets a roadmap for integrating traditional infrastructure into digital and green systems, supporting long-term economic stability .
Funding:
Special Local Bonds: Expected to total RMB 10 trillion in 2025, with a significant portion allocated to green infrastructure.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Increasing reliance on PPPs to alleviate fiscal burdens and attract private investment in smart city projects .
FAI: Manufacturing Investment:
In the grand industrial theater of 2025, China's manufacturing investment takes center stage with a bold choreography targeting 7% year-over-year growth. Like a well-orchestrated performance, this growth story unfolds in three distinct acts, each playing its unique part in the industrial transformation saga.
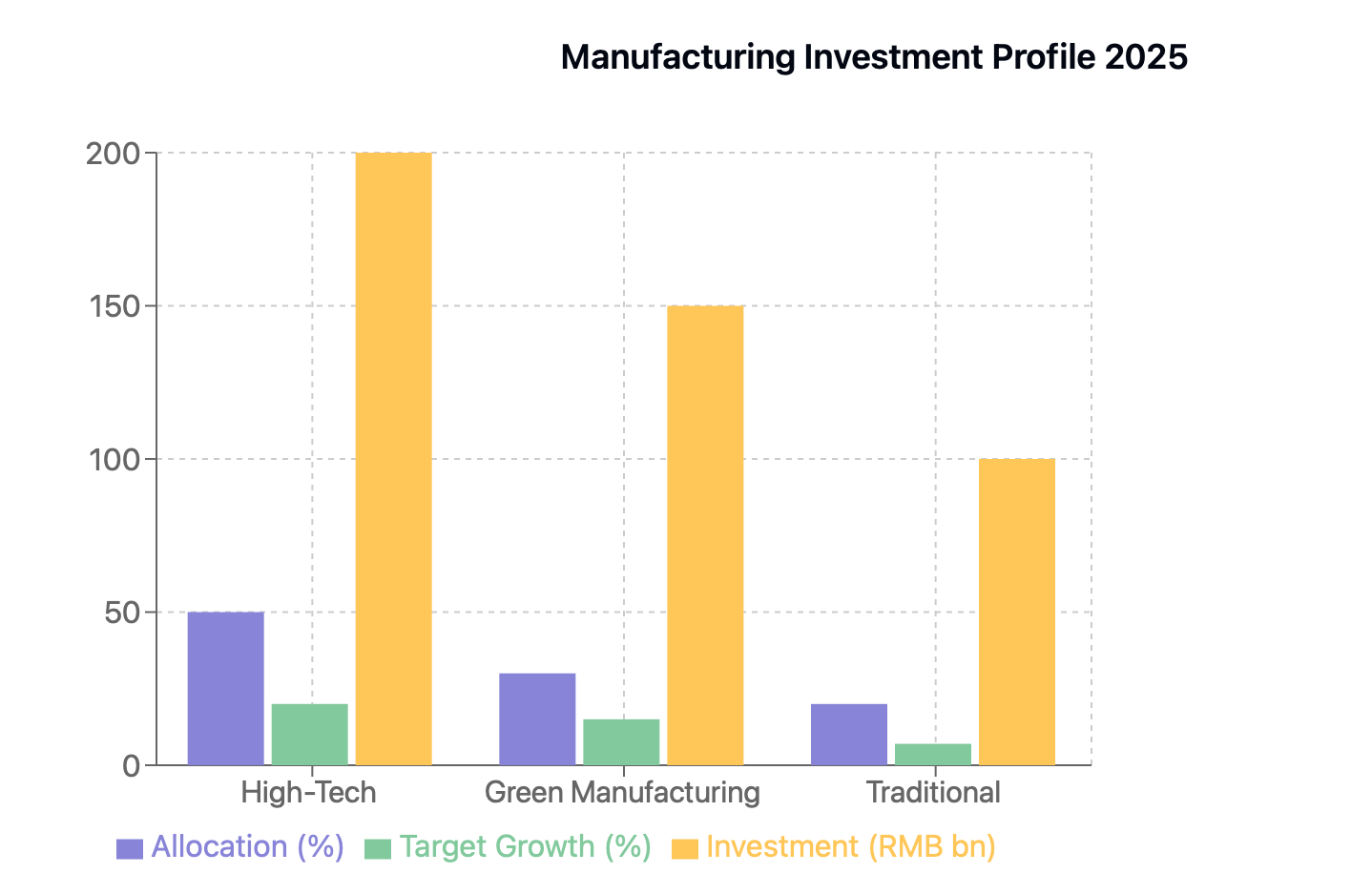
The high-tech sector leads this industrial ballet, claiming 50% of the investment spotlight. Picture semiconductor fabs humming with activity as output surges 20% year-over-year, powered by a robust RMB 200 billion in government subsidies. Meanwhile, robots glide across factory floors with increasing frequency, as domestic robot density pirouettes toward 300 units per 10,000 workers.
Green manufacturing, the production's rising star, commands 30% of the stage. Here, EV battery production capacity expands to a symphony of 1,200 GWh annually, while 50+ hydrogen fuel technology pilot projects scatter across provinces like notes in an ambitious score. This performance aligns perfectly with China's grand finale of carbon neutrality by 2060.
Traditional manufacturing, though playing a supporting role with 20% of investment allocation, undergoes its own transformation. Some 5,000 industrial facilities prepare for their energy efficiency makeover, like veteran performers adapting to a new style of dance.
The storyline interweaves with two strategic themes: the Dual Circulation Strategy, promoting self-reliance in critical technologies, and Global Competitiveness, as China's advanced manufacturing sector seeks to captivate new international audiences beyond traditional markets.
Yet, like any compelling drama, challenges provide dramatic tension. Rising input costs lurk in the wings like demanding critics, while private sector confidence waits for its cue to return to the stage. Success in 2025 will depend on how well policymakers can conduct this complex industrial orchestra through its ambitious performance.
The finale promises a transformation of China's manufacturing landscape - less dependent on traditional rhythms, more attuned to the melodies of innovation and sustainability. Whether this ambitious production achieves its standing ovation will depend on the careful coordination of all players, from state-owned headliners to private sector ensemble members.
Key Metrics:
High-Tech Sectors:
Semiconductor output: Targeting 20% increase YoY, driven by RMB 200 billion in subsidies.
Robotics: Domestic robot density expected to increase to 300 units per 10,000 workers.
Green Manufacturing:
EV battery production: Capacity expansion to 1,200 GWh annually.
Hydrogen fuel technology: Investment in 50+ pilot projects across provinces.
Traditional Manufacturing:
Retrofitting of ~5,000 industrial facilities for energy efficiency.
Policy Integration:
Dual Circulation Strategy:
Encouraging self-reliance in critical sectors like semiconductors and green technologies, reducing dependency on imports .
Global Competitiveness:
High-tech investments align with policies to enhance China’s export competitiveness in advanced manufacturing, targeting non-US markets .
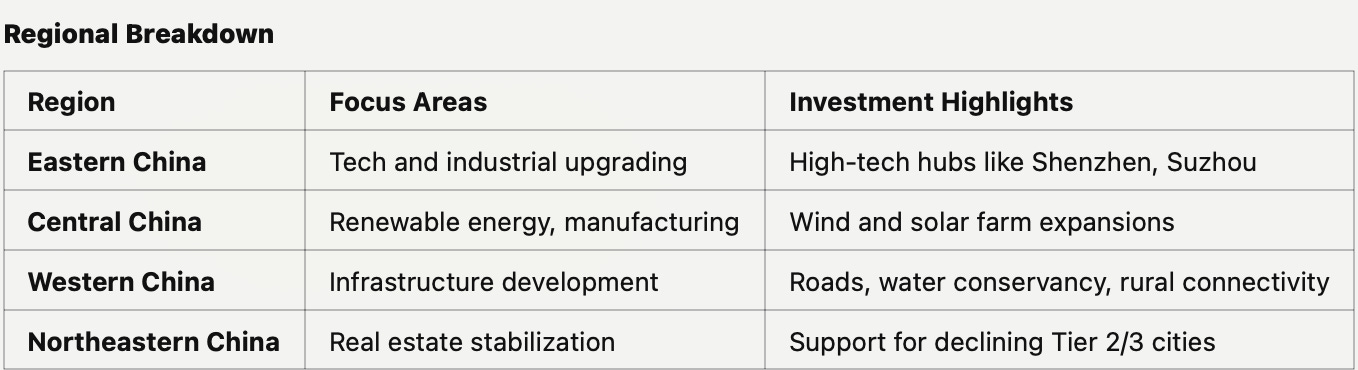
Regional and Real Estate Investment 2025: A Tale of Two Transformations
In the intricate tapestry of China's 2025 investment landscape, real estate and regional development weave together a fascinating narrative of transition and renewal. The property sector, like a phoenix seeking rebirth, shows signs of emerging from its shadows with a modest -2% contraction - a far cry from previous years' deeper declines.
Like a carefully conducted orchestra, the real estate revival plays different tunes across regions. First-time buyers in Tier 2/3 cities find their entry eased by 10-15% reductions in down-payment requirements, while urban village renovations promise to bring new life to approximately 1 million units. The urban housing vacancy rate performs a graceful descent from 14% to 12%, while Tier 1/2 cities anticipate a crescendo of 5-6% in transaction volumes.
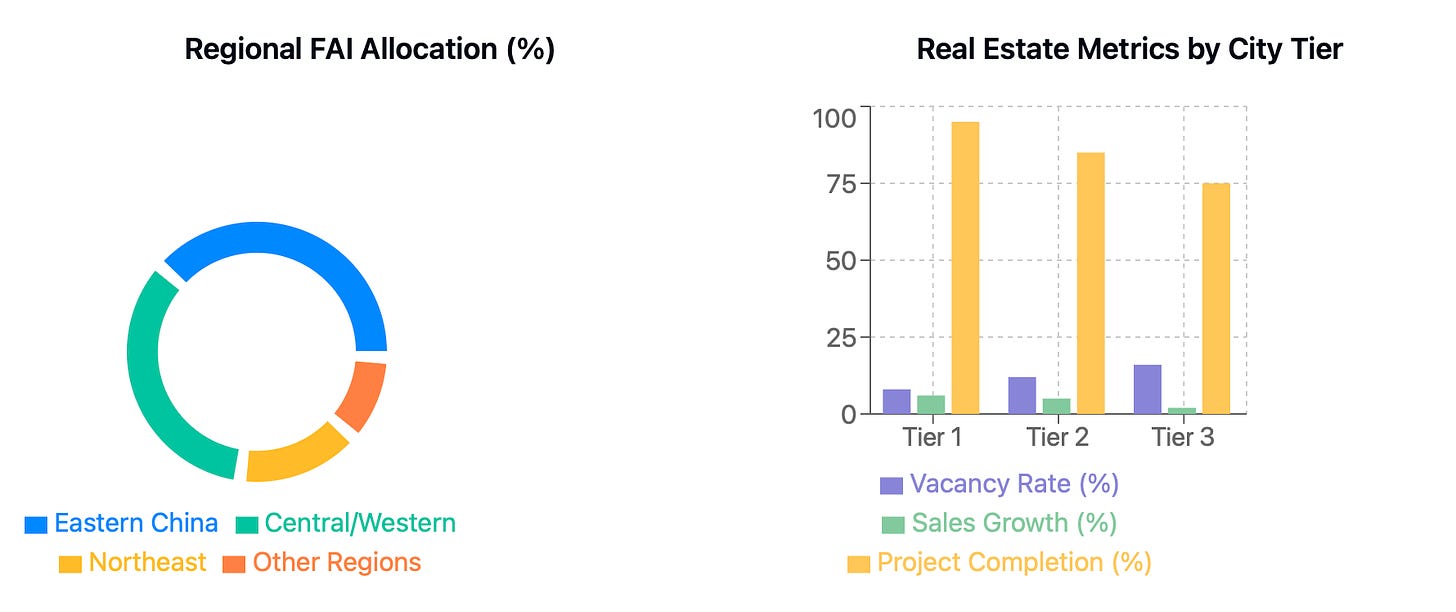
The regional investment story unfolds like a three-act play. Eastern China commands the main stage with 40% of national FAI, its technology hubs and export-oriented manufacturing gleaming like jewels in the spotlight. Central and Western China share a substantial supporting role with 35% of FAI, their renewable energy projects and logistics networks weaving a tale of sustainable development. Northeast China, with 15% of FAI, seeks its own renaissance through industrial revival and property market stabilization.
Yet beneath these broad strokes lies intricate detail: 50 GW of new solar and wind capacity blooming across Western China's landscapes, while 30 new transport hubs in Central China choreograph a dance of improved connectivity. Each investment serves the grand narrative of balanced regional development, supporting the "Go West" strategy's mission to harmonize coastal and inland growth.
Challenges provide dramatic tension - persistent supply overhang in lower-tier cities plays villain to the recovery story, while developers' financial struggles add notes of uncertainty to the performance. But like any well-crafted drama, these challenges serve to highlight the importance of the transformation underway.
RMB 500 billion in credit guarantees stands ready in the wings, preparing to support pre-sold projects and restore consumer confidence. Meanwhile, hukou liberalization in smaller cities promises to expand the audience for housing demand, while the conversion of commercial spaces into residential units demonstrates creative adaptation to market realities.
The success of this dual transformation - both regional and real estate - will ultimately depend on how well these various elements harmonize. As 2025 unfolds, the performance promises to be both captivating and consequential for China's broader economic narrative.
2025 Projection: Contraction narrowing to ~-2% YoY, with stabilization policies providing relief.
Key Metrics:
Housing Demand:
Urban housing vacancy rate projected to decline from 14% to 12%.
Sales recovery: ~5%-6% increase YoY in transaction volume for Tier 1/2 cities.
Developer Support:
Financing relief for pre-sold projects: ~RMB 500 billion in credit guarantees .
Policy Integration:
Social Stability:
Real estate stabilization is central to restoring consumer confidence, crucial for broader economic recovery.
Urbanization Goals:
Real estate policies align with efforts to modernize housing stock and address imbalances between urban and rural housing .
Key Drivers:
Demand-Side Policies:
Reduction in down-payment requirements for first-time homebuyers.
Hukou liberalization in smaller cities to expand housing eligibility .
Supply-Side Adjustments:
Completion of pre-sold housing projects to unlock consumer confidence.
Conversion of underutilized commercial spaces into residential units.
Challenges:
Persistent supply overhang in Tier 3/4 cities.
Developers’ financial struggles due to past defaults and weak sales .
Inflation:
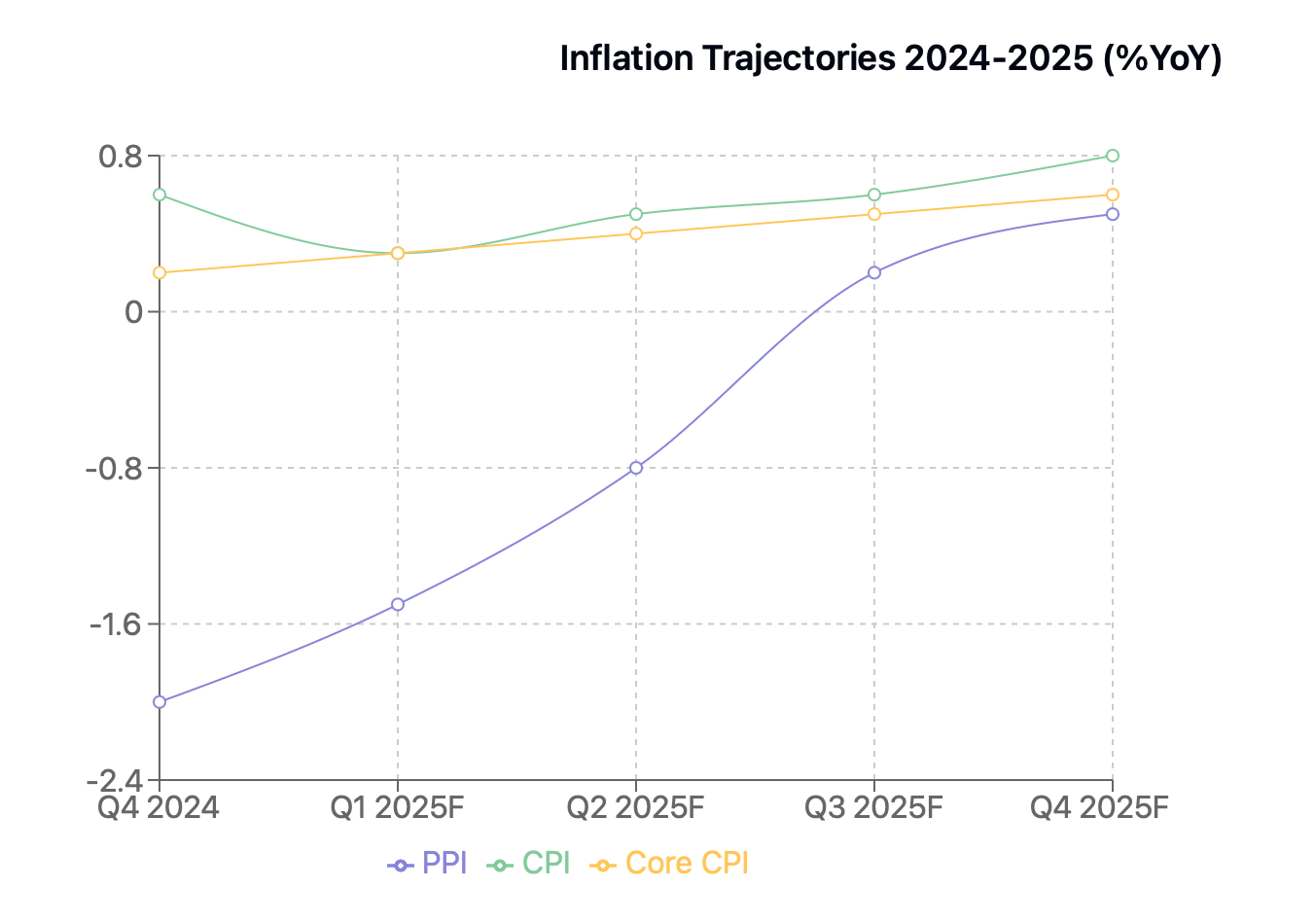
China's 2025 Inflation Outlook: A Tale of Two Indices
In the grand economic theater of 2025, China’s inflation narrative feels less like a blockbuster drama and more like a meticulous character study. Following 2024’s subdued act—where the PPI lingered at a dismal -2% and the CPI tiptoed on stage at a meager 0.5%-0.6%—2025 promises a more balanced, if still understated, performance.
The Producer Price Index, shedding its deflationary malaise, is poised to move from -1.3% to potentially breaking even by year-end. Picture industrial prices dusting themselves off after a long stumble, with green energy materials and high-tech components providing much-needed propulsion. Yet, the pace suggests a cautious vessel still searching for smoother seas.
Consumer prices will keep their deliberate tempo, aiming for a 0.3%-0.8% range. While not headline-grabbing, this slow-and-steady progress aligns perfectly with policymakers’ plans. Core inflation remains predictably restrained, weighed down by languishing housing rents and a recovery in discretionary spending that feels more like a drizzle than a downpour.
China’s policy mix resembles a chef’s precision recipe: 20-40 basis points of interest rate cuts, a 50-100 basis point reduction in the RRR, and a generous helping of fiscal stimulus to stretch the deficit to 4% of GDP. Together, these ingredients aim to stabilize the economy without creating a bubble, balancing liquidity with careful stimulus injections. The goal is not fireworks but a steady glow.
On the industrial side, policies focus on creating strategic growth pillars in renewable energy and semiconductors. This is less about flashy headlines and more about building lasting ecosystems—stable, self-sustaining demand loops that can buttress producer prices in a volatile global market.
Trade, meanwhile, plays the diplomatic card, with a focus on market diversification. The strategy is less about chasing new buyers and more about fortifying resilience against geopolitical shocks, ensuring export pricing power in an increasingly fractious global landscape.
Ultimately, China’s inflation outlook for 2025 is as calm and collected as a Zen garden—minimal volatility, deliberate moves, and a clear focus on long-term stability. By tackling deflationary risks with surgical precision rather than blunt force, Beijing demonstrates that in the world of economic management, boring might just be beautiful.
2025 Monetary Policy Projections
Policy Arsenal 2025: China's Economic Fine-Tuning
In 2025, China's policymakers are orchestrating a carefully calibrated response to inflation dynamics, deploying a sophisticated mix of monetary, fiscal, and industrial tools.
On the monetary front, the PBOC is preparing a precisely measured response: a 20-40 basis point reduction in the Loan Prime Rate, complemented by a 50-100 basis point cut in the Reserve Requirement Ratio. This two-pronged approach aims to reduce borrowing costs while ensuring adequate market liquidity.
Fiscal policy takes a bolder stance, with the deficit target expanding to 4% of GDP. This increased fiscal space enables targeted interventions, from infrastructure spending to consumer subsidies for EVs and appliances. The approach resembles acupuncture rather than surgery - precise interventions at key economic pressure points.
Industrial policy focuses on strategic sectors, particularly renewable energy and semiconductors. This isn't just about supporting individual industries; it's about creating sustainable demand ecosystems that can help stabilize producer prices.
Trade policy completes the toolkit, with a focus on market diversification. This isn't simply about finding new customers; it's about building resilience into China's export pricing power.
The coordination of these tools suggests a sophisticated approach to inflation management - not fighting the last war against high prices, but rather carefully nurturing price stability in an environment where deflation, not inflation, remains the primary concern.
Policy Goals:
Stimulate domestic demand and investment through lower borrowing costs.
Mitigate the impact of external shocks, including US tariff hikes.
Support fiscal initiatives through coordinated liquidity injections.
Expected Adjustments:
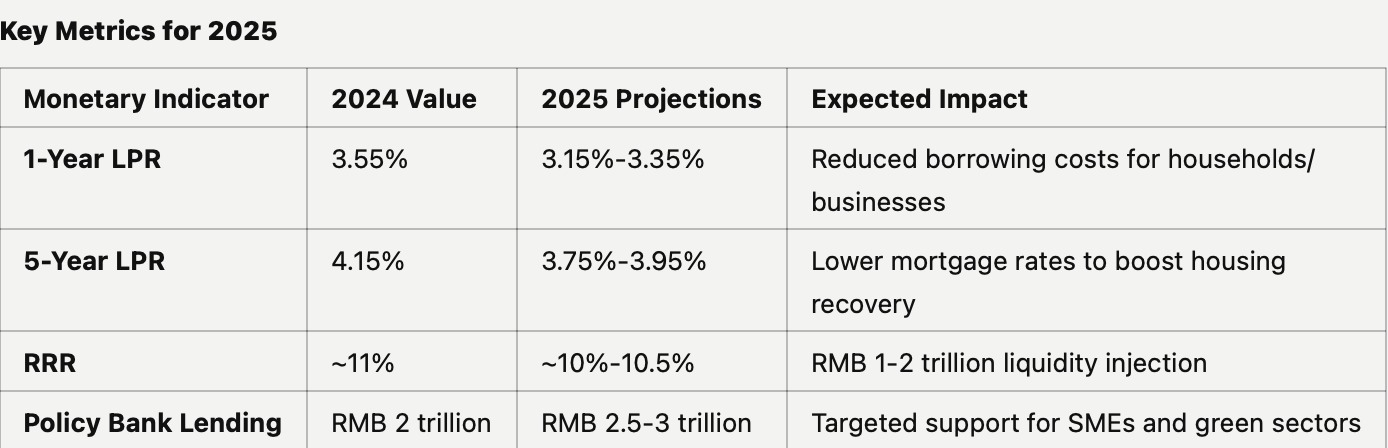
Interest Rates: Further LPR reductions by 20-40 bps. Reverse repo rate cuts of 10-20 bps to maintain interbank liquidity .
Reserve Requirement Ratio (RRR): Anticipated reductions of 50-100 bps, potentially releasing RMB 1-2 trillion in liquidity .
Targeted Monetary Tools:
Policy Bank Lending:
Expanded lending programs for infrastructure, green energy, and technology-driven sectors.
Credit Quotas:
Directed lending to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and strategic industries (e.g., semiconductors, renewable energy)
Fiscal Policy:
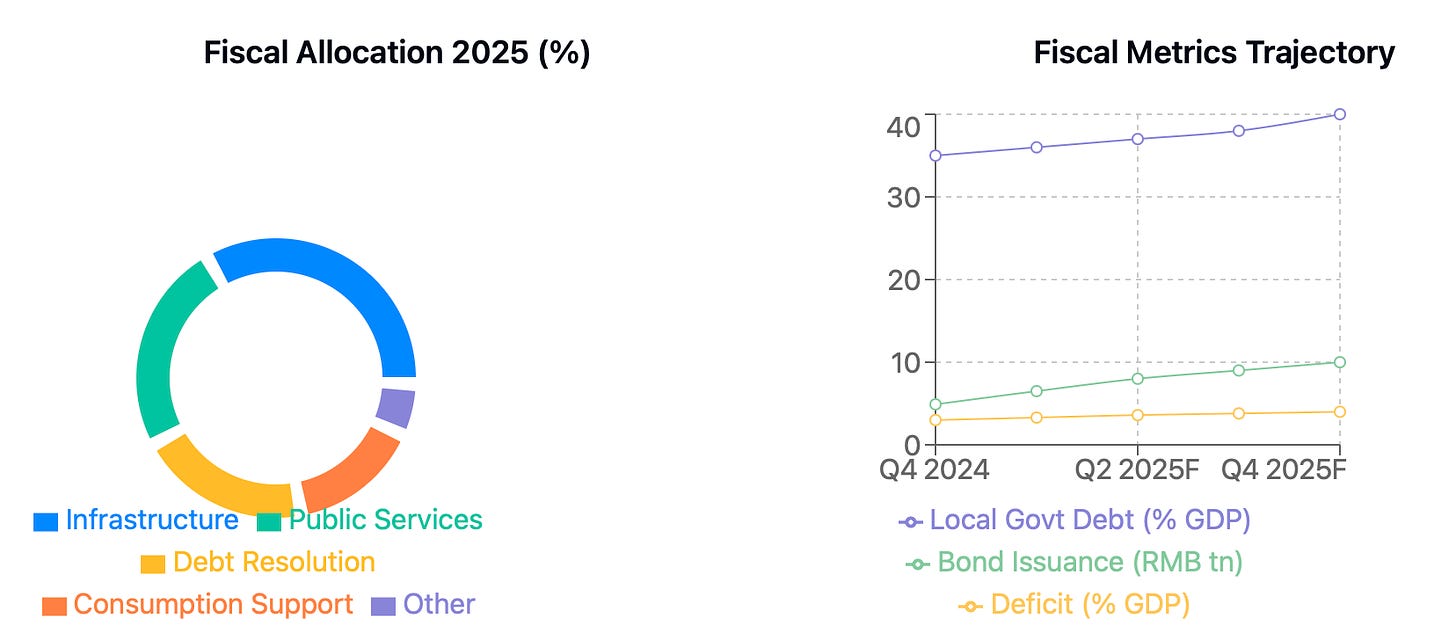
China's 2025 fiscal policy marks a significant shift from tradition, with the official deficit target rising to an unprecedented 4% of GDP. When considering off-budget borrowing and quasi-fiscal activities, the augmented deficit reaches 5.5-6% of GDP, reflecting Beijing's determination to support growth through expanded fiscal channels.
The centerpiece of this fiscal expansion is an ambitious RMB 10 trillion special local government bond issuance – more than doubling 2024's RMB 4.9 trillion. This massive scaling up targets three strategic priorities: digital infrastructure (5G networks, data centers), green development (EV charging networks, renewable energy grids), and traditional infrastructure upgrades.
Public services receive particular attention, with healthcare, education, and social safety net spending projected to grow 7-9% year-over-year. This focus reflects a strategic pivot toward strengthening domestic consumption and social stability.
Local government support emerges as a critical theme, with RMB 2-3 trillion in special refinancing bonds designated for debt resolution. This addresses the twin challenges of maturing debt and weak land sale revenues. Central-to-local transfers are being expanded to ensure fiscal sustainability at the local level.
The consumption stimulus package introduces innovative elements, expanding beyond traditional trade-in subsidies to include direct transfers to low-income households. This targeted approach aims to maximize the multiplier effect of fiscal spending while supporting social equity goals.
Green development receives dedicated fiscal support, aligning with China's carbon neutrality objectives. This includes funding for renewable energy projects, grid modernization, and enhancements to the national carbon trading system.
However, significant risks require careful management:
Debt Sustainability: Local government debt approaching 40% of GDP necessitates strict project prioritization and enhanced oversight.
Revenue Challenges: Persistent weakness in land sales requires diversification of local revenue streams and improved tax collection.
Implementation Risks: The ambitious bond issuance program demands streamlined approval processes and enhanced public-private partnership frameworks.
Integration with monetary policy proves crucial, as RRR cuts and bond yield management will facilitate the massive local government bond issuance. Policy bank lending coordinates with fiscal initiatives to ensure efficient project funding.
This comprehensive fiscal package represents China's most significant stimulus effort since the global financial crisis, yet maintains a clear focus on sustainable, high-quality growth rather than indiscriminate spending. Its success will largely determine the trajectory of China's economic transformation in the latter half of the decade.
2025 Fiscal Policy Projections
Deficit and Spending Targets:
Official Deficit Ratio: Projected to rise to 4% of GDP.
Augmented Deficit: Estimated at ~5.5%-6% of GDP, reflecting increased off-budget borrowing and quasi-fiscal activities .
Bond Issuances:
Special Local Government Bonds: Expected issuance of RMB 10 trillion (vs. RMB 4.9 trillion in 2024). Focused on financing infrastructure projects, especially in green and digital sectors.
Treasury Bonds: Additional issuance to cover deficits and fund public spending .
Key Fiscal Initiatives
Debt Resolution:
Expansion of debt swaps to ease local government fiscal pressures:
Estimated RMB 2-3 trillion in special refinancing bonds to replace maturing debt .
Support for Local Governments:
Increased central-to-local transfers to bridge revenue gaps caused by weak land sale income.
Relaxation of borrowing limits for critical projects .
Targeted Consumption Stimulus:
Expansion of trade-in subsidy programs for consumer goods.
Direct transfers to low-income households to boost consumption .
Green Development:
Allocations for carbon neutrality projects:
Renewable energy projects, grid modernization, and electric vehicle infrastructure.
Strengthened national carbon trading system to incentivize investment in low-carbon technologies .
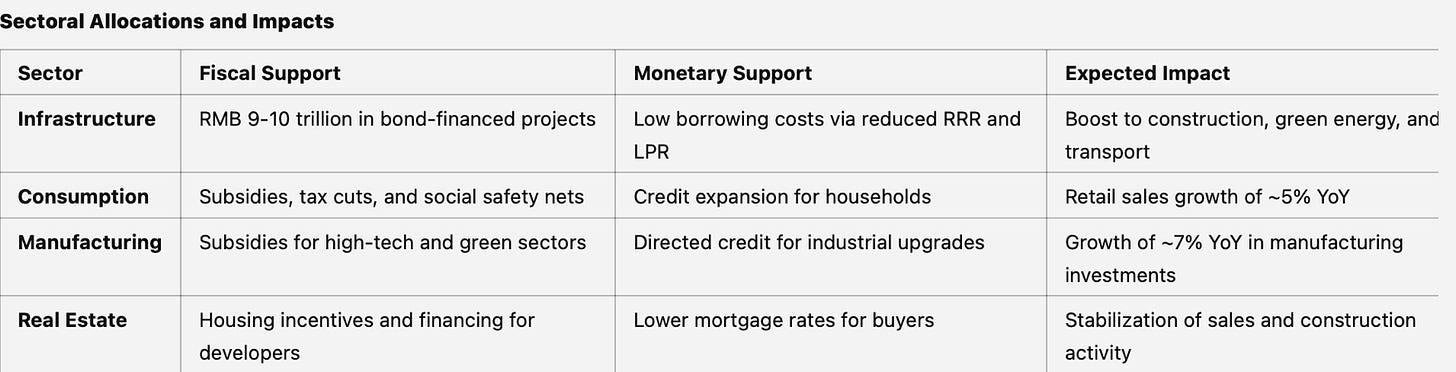
China's 2025 economic strategy demonstrates a masterclass in policy coordination, where fiscal and monetary tools work in concert like a well-rehearsed duet. The RMB 10 trillion special local bond issuance serves as the melody, while monetary policy provides the harmony through precisely calibrated interest rate and RRR adjustments.
The composition features four major movements:
Infrastructure Investment
Fiscal Lead: RMB 10 trillion in special local bonds
Monetary Accompaniment: 20-40 bps LPR reduction and 50-100 bps RRR cuts, releasing RMB 1-2 trillion in liquidity
Tempo: Accelerating through H2 2025
Consumption Support
Fiscal Theme: Direct subsidies and social safety net expansion
Monetary Counterpoint: Lower borrowing costs increasing disposable income
Rhythm: Steady, with emphasis on durable goods and housing
Debt Resolution
Fiscal Motif: RMB 3 trillion in refinancing bonds
Monetary Harmony: Targeted liquidity support through RRR adjustments
Pace: Measured, with careful attention to market stability
Strategic Industry
Fiscal Score: Tax incentives and subsidies for high-tech and green sectors
Monetary Arrangement: Policy bank lending programs
Dynamic: Building momentum toward 15th Five-Year Plan objectives
This coordinated performance aims to achieve multiple objectives simultaneously: stimulating growth, managing debt risks, and advancing structural reforms. The central bank's yield management ensures the fiscal expansion remains affordable, while targeted lending programs direct capital to strategic priorities.
The effectiveness of this coordination will be measured not just in headline growth numbers, but in the quality and sustainability of the economic expansion it generates. Success requires precise timing, careful calibration, and above all, maintaining the delicate balance between stimulus and stability.
Risk factors include potential policy transmission delays, market absorption capacity for the expanded bond issuance, and the challenge of maintaining currency stability. However, the comprehensive nature of the coordination strategy suggests these risks have been carefully considered in the policy design.
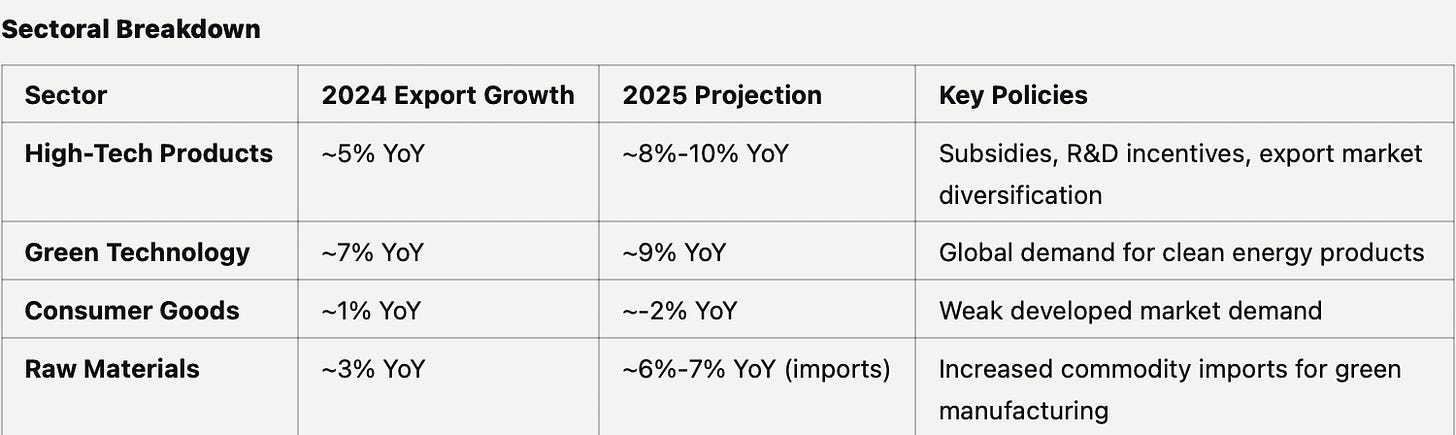
Trade:
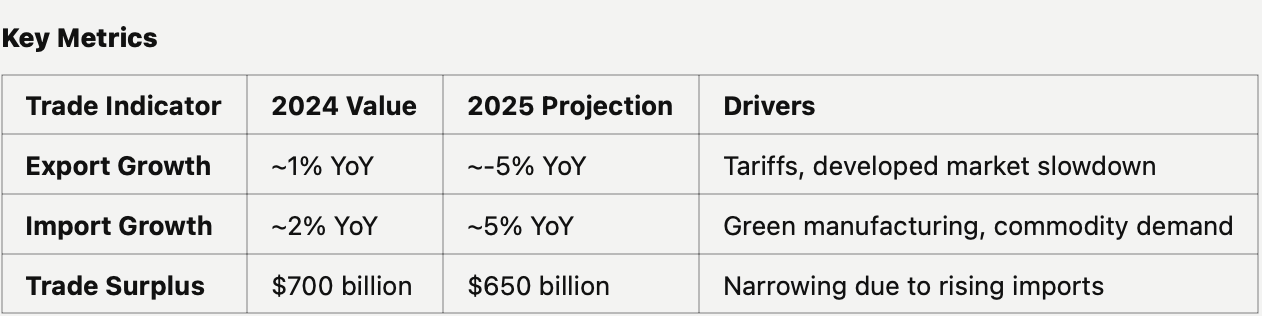
In 2025's complex trade environment, China faces a delicate balancing act between external headwinds and strategic realignment. After 2024's modest performance, the trade landscape is shifting significantly.
Export Trajectory
Overall decline of 5% YoY forecast, primarily due to US market headwinds
Key sectors showing divergent trends:
High-tech manufacturing maintaining resilience
Traditional labor-intensive exports under pressure
Green energy products emerging as growth drivers
Import Dynamics
5% YoY growth projected, reflecting:
Strengthening domestic demand
Strategic raw material procurement
Technology component imports
Notable surge in critical materials:
Semiconductor inputs
EV battery components
Industrial automation equipment
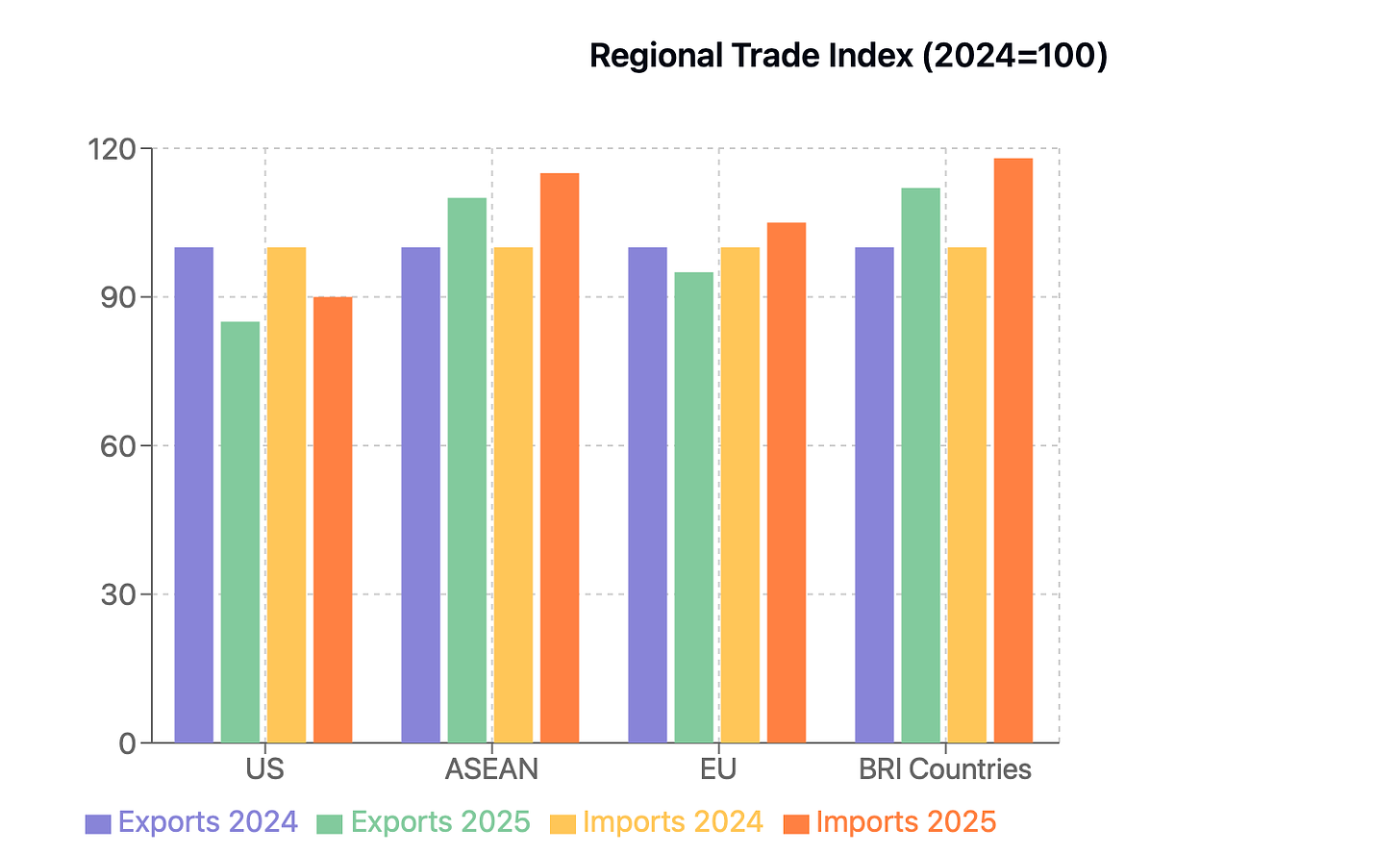
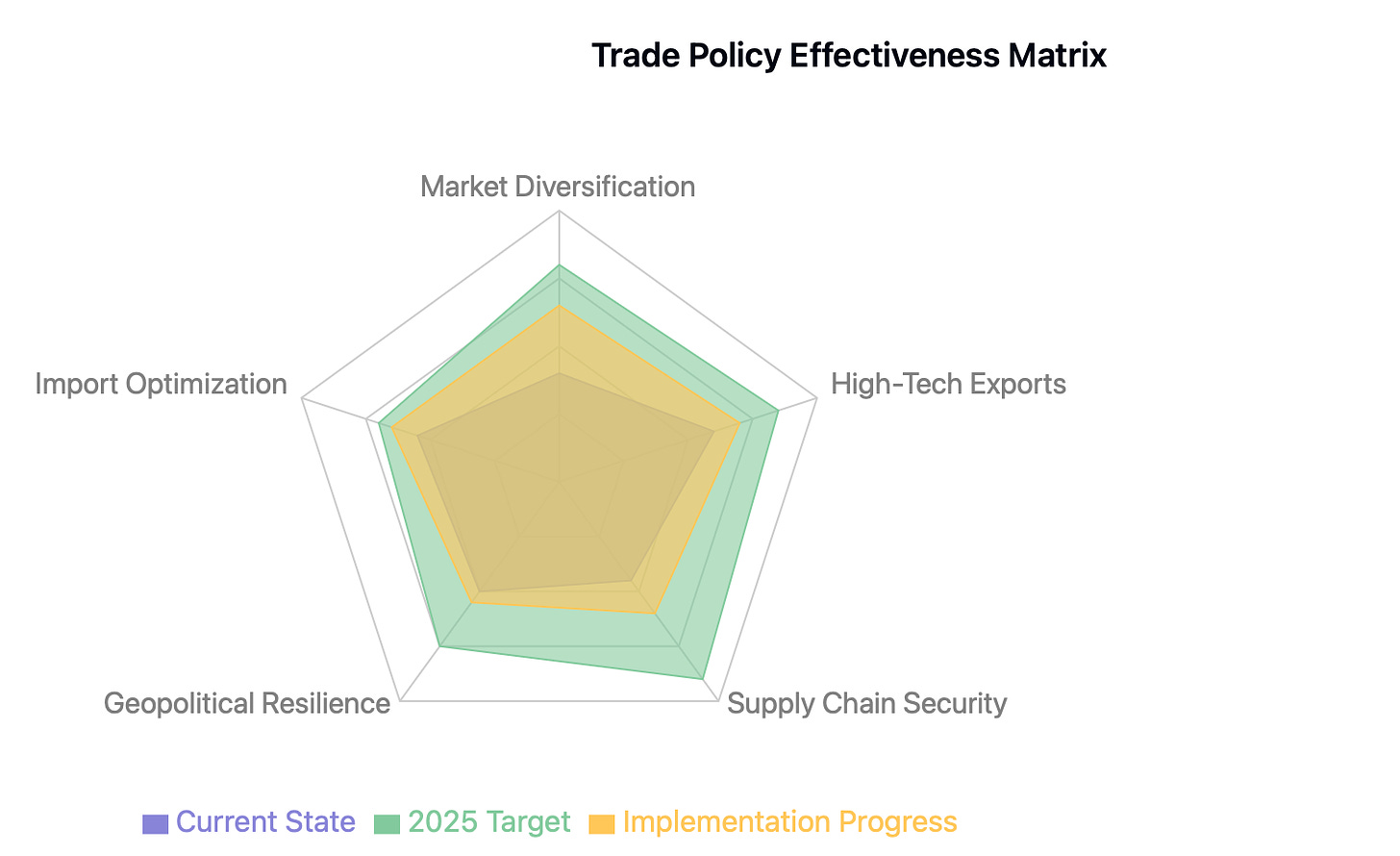
Market Diversification Strategy
ASEAN markets: Target 10% growth
Belt and Road economies: 12% expansion forecast
European Union: Stable with 2-3% growth potential
Emerging market focus: Africa and Latin America presenting new opportunities
Impact Assessment
GDP effect: -0.3 percentage points from trade tensions
Mitigation through:
Domestic market development
Supply chain restructuring
Strategic stockpiling of critical inputs
This evolving trade landscape suggests 2025 will be a year of strategic adaptation rather than pure volume growth, with success measured by market diversification and value-chain positioning rather than headline numbers.
China's 2025 trade policy architecture represents a sophisticated response to evolving global dynamics, with market diversification as its cornerstone. Building on existing Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) foundations, Beijing is actively cultivating deeper trade relationships across ASEAN, Africa, and South Asia, while simultaneously negotiating expanded bilateral agreements with emerging economies. This pivot reflects a deliberate strategy to reduce traditional market dependencies while opening new avenues for growth.
High-value exports form the second pillar of this strategy, with targeted policy support for advanced technology sectors. This includes enhanced export incentives for semiconductors, electric vehicles, and battery technologies, alongside a concerted push in green technology exports. China aims to leverage its established manufacturing capabilities while moving up the value chain, particularly in renewable energy solutions where global demand continues to surge.
Import policies are being carefully recalibrated to support domestic industrial advancement. Tariff reductions on essential manufacturing inputs are being implemented selectively, while simultaneously expanding and securing critical mineral supply chains. This dual-track approach aims to enhance production competitiveness while ensuring resource security, particularly in strategic materials like rare earths and specialized metals.
The framework includes robust geopolitical risk mitigation measures. Strategic export controls on critical materials serve as both economic and diplomatic tools, while intensified engagement with non-US partners helps diversify market exposure. This approach reflects a broader strategy of reducing vulnerability to single-market pressures while maintaining China's position in global supply chains.
These policies are being implemented against a backdrop of evolving global trade dynamics, with success measured not just in traditional export volumes but in the resilience and sophistication of China's trade relationships. The effectiveness of this framework will largely depend on how well it balances immediate economic objectives with longer-term strategic goals in an increasingly complex global environment.
Strategic Implications: Charting China's Course Through 2025 and Beyond
At the intersection of immediate policy actions and long-term aspirations, China's 2025 strategic landscape presents a complex tapestry of opportunities and challenges. The year serves as a critical bridge to the 15th Five-Year Plan (2026-2030), making its success pivotal for China's broader economic transformation.
Structural reforms emerge as the cornerstone of China's strategic vision. The anticipated focus of the 15th Five-Year Plan on technological innovation signals a determined push toward indigenous capability development, particularly in semiconductors, artificial intelligence, and quantum computing. This technological emphasis is complemented by an accelerated green development agenda, targeting not just environmental sustainability but also industrial competitiveness in emerging sectors.
The restructuring of State-Owned Enterprises represents perhaps the most ambitious element of the reform agenda. Beyond mere efficiency improvements, this transformation aims to create more agile, market-oriented entities capable of competing globally while serving national strategic objectives. The success of this reform will significantly influence China's ability to navigate the evolving global economic landscape.
Policy dependencies reveal themselves in the intricate choreography required between fiscal and monetary tools. The expanded fiscal deficit target of 4% and the anticipated monetary easing through RRR cuts must work in concert to achieve the desired economic momentum. This coordination becomes particularly crucial in supporting local government finances while maintaining market stability.
However, the risk landscape appears increasingly complex. Geopolitical tensions, particularly in technology access and trade relations, could significantly impact the pace of innovation-driven growth. Local fiscal constraints, despite central government support, may limit the effectiveness of stimulus measures. The property sector's gradual recovery path could continue to weigh on consumer confidence and local government revenues.
Looking beyond 2025, several strategic questions emerge:
How will China balance technological self-sufficiency with international cooperation in an era of increased competition?
Can the green development push create sufficient new growth drivers to offset traditional industry decline?
Will SOE reforms successfully navigate the tension between market efficiency and strategic control?
How might evolving demographic trends influence the success of consumption-led growth strategies?
The answers to these questions will likely determine not just China's economic trajectory through the remainder of the decade but also its position in the global economic order. Success will require not only effective policy execution but also the ability to adapt strategies as circumstances evolve.
2025 thus stands as more than just another year in China's development - it represents a crucial period of transition, where the effectiveness of near-term policies will largely determine the feasibility of longer-term strategic ambitions.
Panda Perspectives: China 2025 - A Data-Driven Macroeconomic Outlook
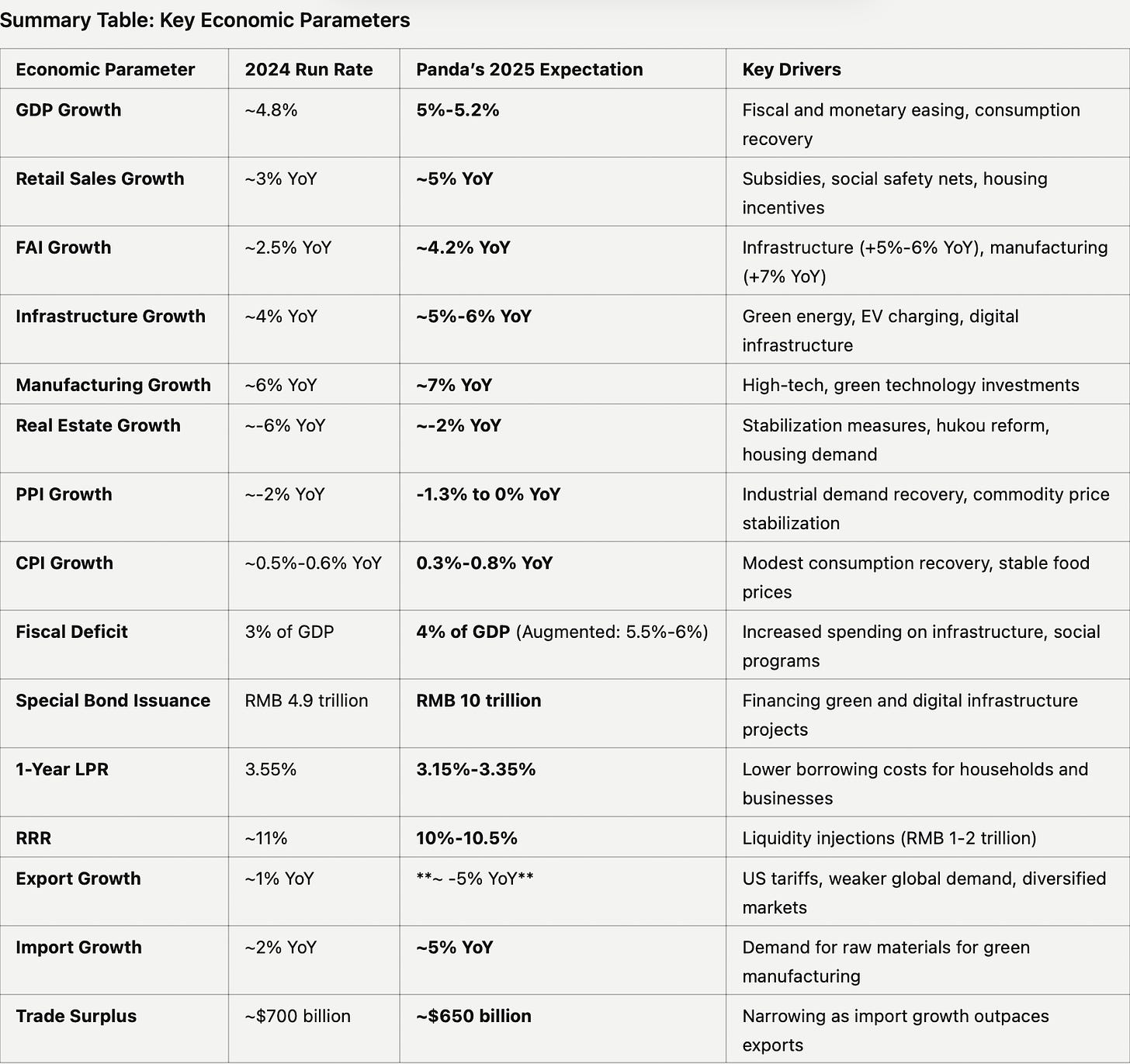
2025 presents a pivotal year for China’s economy, with a delicate balance between policy-driven growth and significant structural challenges. The government is targeting GDP growth of 5%-5.2%, driven by fiscal and monetary interventions aimed at stabilizing consumption, boosting investments, and navigating external trade pressures. However, hurdles such as geopolitical tensions, high local government debt, and lingering real estate weaknesses pose risks to the recovery trajectory.
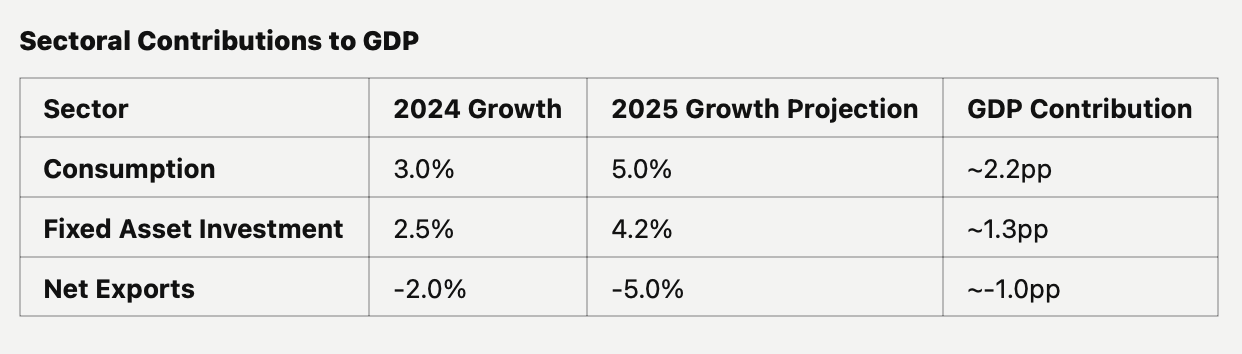
Consumption will be a key growth driver, with retail sales expected to grow ~5% YoY, supported by subsidies, tax reforms, and expanded social safety nets. Spending will benefit from programs targeting durable goods, novel consumer sectors like the “Silver Economy,” and childcare incentives. Meanwhile, fixed asset investment (FAI) is projected to recover to ~4.2% YoY, led by infrastructure growth of 5%-6% and manufacturing expansion of ~7% YoY in high-tech and green industries. Real estate investment, while still contracting, will see a narrower decline of ~-2% YoY, aided by stabilization measures.
Inflation is expected to remain muted, with the Producer Price Index (PPI) turning positive in the second half of the year and the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reaching 0.3%-0.8% YoY. Fiscal policy will play a central role, with an augmented deficit of 5.5%-6% of GDP and bond issuances of RMB 10 trillion to finance infrastructure and social programs. This will be complemented by monetary easing, including anticipated reductions in the Loan Prime Rate (LPR) by 20-40 basis points and Reserve Requirement Ratio (RRR) cuts of 50-100 basis points, injecting RMB 1-2 trillion in liquidity.
Trade remains a challenging area, with exports projected to decline ~5% YoY due to US tariff hikes and weakening global demand. Imports, however, are expected to grow ~5% YoY, driven by demand for raw materials supporting green manufacturing. The government will focus on diversifying trade relationships with ASEAN, Africa, and South Asia, while emphasizing high-tech and green technology exports.
Despite these efforts, risks remain. Geopolitical tensions could disrupt export markets, while high local government debt, projected to reach ~40% of GDP, may constrain fiscal flexibility. The government’s success in implementing its Dual Circulation Strategy and laying the groundwork for the 15th Five-Year Plan will be critical in ensuring sustainable growth.
In sum, China’s 2025 economic outlook reflects an ambitious yet cautious recovery, leveraging targeted policies to mitigate risks and unlock growth opportunities. As always, the interplay of policy execution, global dynamics, and domestic resilience will define the success of this trajectory. For investors, the focus will be on monitoring key sectors like green energy, high-tech manufacturing, and consumption to navigate both opportunities and challenges








Appreciate the effort but I find the extra flourished language a bit distracting and repetitive like it was indiscriminately added with a GPT. Would prefer just the info with flourished language only added if a datapoint really stands out.